L38. Hearing Flashcards
Describe hearing loss severity to the loss of different frequency detection
A loss of low frequency detection is regarded moderate relative to normal while a loss of high frequency sound is indicative of severe/profound hearing loss

What is the symptom described by patients beyond mild hearing loss?
Lots of difficulty discriminating words
What is being detected by humans in terms of sound energy to characterise:
- Pitch
- Loudness
- Timbre/Tone/Resonance
- Pitch = Wavelength/frequency
- Loudness = amplitude
- Resonance = Waveform
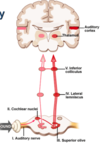
Recall the anatomy of the auditory system in terms of the chambers and the major components that make up hearing (draw a diagram)

Describe the general path of sound energy waves picked up by the auricle through to the neural signal sent through to the auditory cortex of the brain
- Sound energy waves picked up by auricle
- Sound energy converted into mechanical energy at the tympanic membrane
- The tympanic membrane transmits this energy through the three ossicles and then to the oval window
- The oval window is the interface for mechanical vibrations being converted into energy vibrating through fluid
- Fluid movement is sensed by specialised hair cells in the cochlear
- Hair calls convert this movement into a neural signal to be transmitted to the brain
What is the main nerve carrying this information to the auditory cortex?
The vestibulocochlear nerve CN VIII (through the cochlear division of the nerve)
What is one of the important functions of the auricle?
To localize sound particularly in the vertical domain
What normally happens to sound travelling through air as it reaches a fluid interface? (And thus what does the ear have to overcome?)
Normally sounds passing from air to fluid become dampened significantly as over 90% of the sound energy is reflected at the interface.
Thus the apparatus of the ear has to overcome this loss of energy
What is impedance matching? What structure(s) of the ear are important for this?
Impedance is the level of resistance through a circuit.
Impedance matching is matching the waves of sound in air to the movement of sound in fluid (ie. matches the impedance of air to the impedance of fluid within the ear)
The ossicles are important for this
Describe how the ossicles of the ear achieve impedance matching
The size of the tympanic membrane is very large relative to the oval window (20:1) this means that there is a large pressure difference generated between them through the ossciles.
The lever action of the ossicles of 1:3:1 generates a force difference
There pressure and force at the oval window is about 200 fold greater than that of the hitting the air at the tympanic membrane
Describe the spiral arrangement of the cochlea in relation to the ganglion of the auditory nerve
The cochlear makes 2.5 revolutions

What are the three chambers of the cochlea of the inner ear?
- Scala vestibuli - filled with perilymph
- Scala media - filled with endolymph
- Scala tympani - filled with perilymph

What are the two membranes in the cochlea, describe their locations
Both membranes are located between the scala tympani and the scala media
- Basilar membrane is located just above the scala tympani
- Tectorial membrane is fixed in place and is located just under the scala media (on top of the basilar membrane

How are the basilar membrane and tectorial membrane involved in sound reception?
The movement of fluid through the cochlear moves the basilar membrane in relation to the tectorial membrane and this relative movement is detected by hair cells, which transduce it into a mechanical signal.
Describe the anatomy of the basilar membrane
The basilar membrane is like a flipper
- It is wider at the apex (the ‘tip’) of the cochlear and narrower at the base.
- This arrangement means that the base is stiff and the apex is very floppy

What does this difference in physical properties between the apex and base of the basilar membrane mean for the response to sound of each part?
The Base is stiff and thus will require more energy to move it (only responds to high frequency)
The Apex is more floppy/thick and thus requires less energy to move it (only responds to low frequencies)
All sounds can be encoded on the basilar membrane based on the anatomy and location. What is important about this organisation?
It is retained throughout the whole auditory system (a tonotonic map/topography).

What is the organ of Corti
The sensitive element in the inner ear situated on the basilar membrane: it contains rows of hair cells protrude from the surface, it is responsible for the transduction of electrical signals
Where do the auditory receptors/hair cells lie?
They are sandwiched between the basilar membrane and the reticular lamina of the tectorial membrane.
Hair cells are embedded in the basilar membrane with sterocilia projections in the tectorial membrane

What are the different types of hair cells? What are their locations?
- Inner hair cells: sit in a row closer to the afferent axon fibres of the cochlea nerve and feed directly into them
- Outer hair cells: sit further away from the afferent axons and receive efferent information from the brain for modification of sound pathways

Each hair cell has about 100 sterocilia projecting from it. What is the significance of this?
They extend over the top of the hair cells and insert into the tectorial membrane. They are what detect movement and direction of movement/oscillation.
The bending of sterocilia causes neuronal signalling
Describe the arrangement of sterocilia on the hair cells
The sterocilia are not all the same length. They are arranged in length/height order with the longest one called the kinocilium

Describe how travelling waves through fluid initiate auditory transduction
Sound induced vibration causes a particular end the basilar membrane to move up and down in response.
This movement creates a shear force of the hair cell sterocilia on the tectorial membrane. Oscillation in one direction causes the sterocilia to bend towards the kinocilium, oscillation in the other direction will have the opposite effect.
The frequency of this movement and the amplitude of it is converted into neural signals

Describe the normal state of a hair cell in terms of potassium channels
Potassium channels are open all the time in hair cells (this is opposite to other cells of the body)