Lab 6 Flashcards
(39 cards)
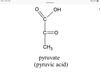
Pyruvate
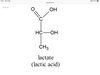
Lactate
Acetyl-CoA

Oxaloacetate

Citrate

Alpha-ketoglutarate

Succinate

Fumarate

Malate

Hypoxanthine

Xanthine

Uric acid

Biological oxidation
Processes which take place in the mitochondria of the cell
What starts the process of biological oxidation?
Transfer of hydrogen from the substrate to a hydrogen carrier coenzyme (NAD+, NADP+) or prosthetic group (FAD, FMN)
The most important processes producing reduced coenzymes and prosthetic groups are…?
The citric cycle, beta-oxidation, and the PPP
Where does the reduced coenzymes take the hydrogen?
to the respiratory chain in the inner mitochondrial membrane
takes up oxygen and turns to water
Aerobe dehydrogenases + example
enzymes that can take hydrogen directly to the molecular oxygen to release H2O2
example: xanthine oxidase
How can biological oxidation be demonstrated?
manomeric method
using electrodes that show the changes of the pO2
using a dye that has a different color in its reduced and oxidized form
Which redox dye will we use in the lab, and what does it accept hydrogen from?
2, 6-dichlorophenolindophenol
from reduced flavoproteins (FMNH2, FADH2)
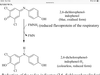
Reduction of redox indicator
What color is the oxidized form of 2,6-dichlorophenolindophenol?
Blue
What color is the reduced form of 2,6-dichlorophenolindophenol?
(2,6-dichlorophenolindophenol-H2)
Colorless
What does the time of fading of 2,6-dichlorophenolindophenol depend on?
What is the substrate in the demonstration of the biological oxidation?
Glucose, lactate or succinate


