LEC-3 MSK Embryology Flashcards
(87 cards)
The mesoderm for the skeletal system comes from what two sources?
- Paraxial mesoderm
- Parietal mesoderm
The skeletal system is formed from what two embryonic tissues?
- Mesoderm tissue
- Neural crest tissue
Somitomeres and somites are formed from which mesoderm?
Paraxial
Which mesoderm becomes fused to the body wall once folding of the embryo occurs?
Parietal
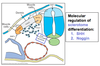
What two signal transduction pathways regulate the differentiation of mesenchymal cells into sclerotome, or cells that form the vertebral arch?
- SHH (Sonic Hedgehog)
- Noggin

Cells at the ____________ and _____________ tips of a developing somite differentiate into precursor muscle cells, known as the _________.
- Dorsomedial and ventrolateral.
- Myotome
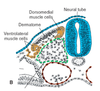
Cells intervening between the ventrolateral and dorsomedial tips of the developing somite differentiate into precursor skin cells known as the ______________.
Dermatome
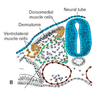
_________ and _________ are two key encoding genes that produce proteins vital for muscle differentiation in developing embryos.
MyoD and MYF5
In general, what forms the face and part of the skull?
Neural crest

In general, what forms the axial skeleton from somites and part of the skull from somitomeres and occipital somites?
Paraxial mesoderm

In general, what forms the limbs, sternum, and the pelvic and shoulder girdles?
Parietal mesoderm (body wall)

What are somitomeres and somites?
The segmentally arranged clusters of cells derived from mesoderm and located along the axis of the developing embryo
(Somites/Somitomeres) are located from the occipital region to the coccyx in the developing embryo. They are small and tightly organized.
Somites
(Somites/Somitomeres) are located in the head region of the developing embryo. They are large and loosely organized.
Somitomeres
The vault of the skull refers to the (chondrocranium/membranous neurocranium/viscerocranium).
Membranous neurocranium
Through what method is the neurocranium formed?
Formed through direct intramembranous ossification (meaning cartilage is not present during ossification).

The face refers to the (chondrocranium/membranous neurocranium/viscerocranium).
Viscerocranium
Through what method is the viscerocranium formed?
Formed by endochondrial ossification (meaning cartilage is present during ossification) AND intramembranous ossification (meaning cartilage is not present during ossification)
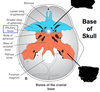
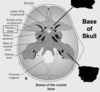
The base of the skull refers to the (chondrocranium/membranous neurocranium/viscerocranium).
Chondrocranium
Through what method is the chondrocranium formed?
Formed by endochondrial ossification (meaning cartilage is present during ossification).
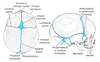
Identify which of the following structures are derived from the neural crest.
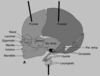
Neural crest structures are shown in blue.

Identify which of the following structures are derived from the paraxial mesoderm.

Paraxial mesoderm structures are shown in red.

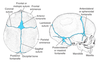
Identify which of the following structures are derived from the parietal mesoderm.

Parietal mesoderm structures are shown in yellow.

Identify which of the following structures are derived from the paraxial mesoderm.

Paraxial mesoderm structures are shown in red.
- Base of skull = Chondrocranium