Lecture 1 - Principles of Strategic Planning Flashcards
(22 cards)
What is strategy? What are the characteristics of strategic decisions?
- Strategy is the overall plan for deploying resources to establish a favourable position
-
Characteristics of strategic decisions:
- Important
- Involve a significant commitment of resources
- Not easily reversible
What makes a succesful strategy?
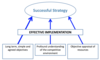
Show how strategy can be used as a link between the environment and the firm

Illustrate the thought process of deciding between going for a business strategy or corporate strategy.

What are the multiple roles of strategy?
Decision support: improves quality of decision making
Coordination & Communication: creates consistency & unity
Target: improves performance by setting high aspirations
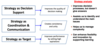
Explain what is meant as strategy as positioning and strategy as a direction.
Positioning
- Where are we competing?
- How are we competing?
Direction
- What do we want to become?
- What do we want to achieve?
- How will we get there?

Draw the industry life cycle graph ( x: Time, y: Industry shares)

Draw a graph showing how product and process innovation varies over time.

How typical is the life cycle pattern?
illustrate this with life cycles of television (x: time, y: sales)
- Industry life cycles have become increasingly compressed (e.g., e-commerce) and patterns of evolution might differ.
- Some industries (especially those providing basic necessities, e.g. food processing, construction, apparel) reach maturity, but not decline
- Industries may experience life cycle regeneration
- Life cycle model can help us anticipate industry evolution – but dangerous to assume any common, pre-determined pattern of industry development

In many industries, what is the impact of companies that are started as spin offs from employees?
- 20% started as spin offs from employees
- outperform de novo entrants
- a large proportion of the industry leaders
- play a major part in shaping business models and industrial structure
- Spin-offs are critical in the manufacturing industry
- Auto, tyre and semi-conductors in the US (technology intensive)
- Cotton in Bangladesh (less technology intensive)
Explain the UK’s productivity puzzle
The productivity-puzzle
- Average growth in labour productivity has fallen
- Productivity gap between frontier and non frontier businesses is growing
- UK productivity by sector is dominated by aerospace, automotive, pharma, services, manufacturing etc.
- Manufacturing as a share of GDP has been declining
- Manufacturers becoming increasingly servitised
- Manufacturing R&D as a percentage of GDP is low
- UK R&D as a percentage of GDP is low
- Patents granted is low
- Punches well above its weight in terms of research
- Ranked as one of the best places to start a business

What is the UK industry poor at? (or doesn’t do much of it)
- Patent Grants low
- UK’s R&D as percentage of GDP low

Give some facts about the UK’s research compared to the world.
The UK accounts for:
- 1% of Global population
- 3.2 per cent of global R&D expenditure
- 4.1% per cent of global researches
- 8% of papers published
- produce 6.4% of worlds research articles
- 16% per cent of the worlds most highly cited papers

UK is one of the best places to start and grow a business.

What are the causes of the productivity paradox?
- Slowdow in technological diffusions across firms
- Skills mismatch due to changes in the product market structures
- Legacy of financial crisis
- Mismeasurement due to digital economy
- As digital economy grows it is harder to add value intangibles
- Lack of business model innovation
What are the impacts of brexit for the UK
- Vision of ‘Global Britain’
-
Single market
- free movements of goods, capital, services and people
- economic policy harmonisation (e.g. health and safety legislation and monopoly & competition policy)
-
Customs union
- no customs duties are levied on goods moving within the member states
- members of the customs union impose a common external tariff on all goods entering the area
-
Impact on
- R&D spending and scientific research
- foreign investment in the UK
- supply chain
- demand for goods
- Negotations about whether UK should still be part of the customs union despite brexit so it doesnt experience tax on imports/exports.
- If UK exports/imports outside of the EU then not being part of customs union will be beneficial.
What are the two processes for studying strategy?
INTENDED STRATEGY (DESIGN)
- Planning and rational choice
EMERGENT STRATEGY (PROCESS)
- Many decision makers responding to a multitude of external and internal forces
intended + emergent –> realised strategy
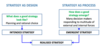
What is the planning perspective?
- Driven by senior management who set strategic direction for the whole company
- Rational process heavily driven by empirical models and concepts
- Intentionally designed
- Formally structured and comprehensive
- Future to be predicted and anticipated
What is the emergence perspective?
- Driven by vision and organisational learning
- Process of adaptive persistence where strategic direction evolves from incremental adjustments to evolving events
- Unstructured and gradually shaped
- Experimentation and parallel initiatives
- Future partially unknown and unpredictable
Give the Intel story of how it moved from being a DRAM to a microprocessor manufacturer.
(DRAM = Dynamic Random Access Memory)
- Japanese calculator company, Busicome wanted a chipset designed for its calculator.
- Intel purchased the rights from Busicom
- Enormous importance of PC not evident
- IBM chose 8088 microprocessor for its first personal computers.
Resource allocation drove strategic action
- Intel saw the margins for the memory business shrinking and the computer industry growing.
- The memory and semiconductor business shared fabrication plants (Intel didn’t need new factories to make microprocessors)
- Margin-per-wafer start did not maximize immediate profits but selected niche over commodity markets ( PC market was niche at the time)
- Since microprocessor had a higher margin it gradually was provided more resources in factories - resulting in exit from DRAM.
Resource allocation method provided alignment between internal and external conditions
Describe the HONDA story, from both BCG and Pascale interpretations.
(BCG = Boston consulting group)
- BCG: Honda entered the US Market with the small 50cc which it used to establish a foothold.
- Pascale: Honda tried to sell larger bikes, but couldnt so it started to sell the 50cc.
- BCG: Honda redefined the motorcycle market by targeting the ordinary person and distributing them through bicycle shops
- Pascale: Honda reluctantly chose the “nicest people campaign” developed by a UCLA undergraduate. Sold through bicycle shops because results were not good through traditional channels.
- BCG: Honda followed a policy of developing the market region, by region. The started on the west coast and moved eastward.
- Pascale: Honda chose LA where there was a large second & third generation Japanese community, a suitable climate and a growing population.
Some people say there where successful because they had a rational strategy. Others say they learnt from mistakes through an emergent strategy.
What are Mintzberg’s critique of formal strategic planning?
- The fallacy of prediction – The future is unknown, forecasting limited, assumes future ressembles past, creates strategies likely to disintegrate with events
- The fallacy of detachment – Impossible to divorce formulation from implementation, planners tend to be focussed on hard data and measuring what is measurable.
- The fallacy of formalisation – Inhibits flexibility, spontaneity, intuition and learning. By overstructuring and emphasising logic we can end up with a small variety of options. Planning defines categories, creativity creates them.


