Lecture 5 - Resources and Capabilities Flashcards
(25 cards)
What did Porter’s critics say?
Empirical evidence suggests that only a small percentage of variances in profitability is explained by industry differences
Firms might not adopt generic strategies
- Firms do pursue multiple generic strategies (e.g. Dell)
- Successful differentiators can become cost-leaders
- Quality and low cost can be combined in different ways
- In some markets cost is largely irrelevant (e.g. digital technologies where MC =0)
Competitive analysis seems insufficient in developing expectations about the value of a future resource to be acquired (e.g. at a cost significantly below its economic value)
An ‘efficient market hypothesis’ type logic suggests that even if some industries are more profitable than others, they cannot be so for long.
What is the rationale for the resource based approach to strategy?
Rationale for resource-based approach to strategy
- When industry environment is volatile, internal resources and capabilities offer a more stable basis for strategy than an industry or market focus
- A firm’s competitive position is defined by a bundle of unique resources and relationships
- Resources and capabilities are the primary sources of profitability
- The trick is to configure these resources in such a way that they are costly, difficult, or indeed impossible to imitate or transfer
- The task of management is to renew these resources and relationships as time and competition erode their value
- Corporations are successful as long as their capabilities remain relevant, distinctive and highly valued
What qualities do resources need to be to strategically important?
VRIN
Valuable – When resources are able to bring value to the firm they can be a source of competitive advantage
Rare – Resources have to deliver a unique strategy to provide a competitive advantage to the firm as compared to competing firms
Inimitable – Resources can be sources of sustained competitive advantage if competing firms cannot obtain them
Non-substitutable – resources should not be able to be replaced by any other strategically equivalent valuable resources.
Explain the links between resources, capabilities & competitive advantage
Links between resources, capabilities & competitive advantage
Competitive advantage + industry key success factors
= strategy = organisational capabilities
RESOURCES
Tangible: financial, physical
Intangible: technology, reputation, culture
Human: skills/know how, capacity for communication & collaboration, motivation
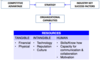
What are the two ways of identifying organisational capabilities?
Organisational capabilities: using your resources effectively.
A functional classification
- Corporate functions
- Information mgmt.
- R&D
- Operations
- Design
- Marketing
- Sales and distribution
Value chain classification
Primary activities + support activities

How are resources integrated to form organisational capabilties?
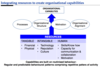
Integrating resources
- Tangible (physical, financial)
- Intangible (technology, reputation, culture)
- Human (skills/know how, capacity for communication & collaboration, motivation)
To produce
Processes
Organisational structure
Motivation
Organisational alignment
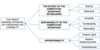
What factors effect the profit earning potential of a resource?
The profit earning potential of a resource or capability is a function of:
- The extent of the competitive advantage established (scarcity, relevance)
- The sustainability of the competitive advantage (durability, transferability, replicability)
- Appropriability (property rights, relative bargaining power, embeddedness)
Explain evolutionary economics and dynamic capabilities
Evolutionary economics views decisions made by a firm as determined by established routines
- Routines include methods of production, hiring policies etc.
- Usually a firm’s routines change slowly over time (if they do change)
- To ensure survival, firms need to continuously improve their routines
Firms with dynamic capabilities can adapt their resources and capabilities and exploit opportunities created by market shocks and discontinuities
Explain the micro-foundations of dynamic capabilities
Sensing
Analytical systems (and individual capacities) to learn and to sense, filter, shape and calibrate opportunities
Identification and assessment of opportunities
Seizing
Enterprise structures, procedures, designs and incentives for seizing opportunities
Mobilising resources internally and externally to address opportunities and capture value
Transforming
Continuous alignment and realignment of specific tangible and intangible assets
Continued renewal of the organisationE

What are factors that limit dynamic capabilities?
A firm’s dynamic capabilities are inherently limited because of
- The path dependence of sources of competitive advantage
- The limited availability of complementary assets
- “windows of opportunity” that do not stay open for long
Explain reasons for the imitation strategy?
- Incumbents are more likely to respond to innovation in their industry when their counterparts do so
- Incumbents are affected by the entry of firms that are similar in size and resources
- When a higher similar company enters the new market, it raises the probability that the company enters itself beyond levels based solely on the attractiveness of the market.
Explain how to sustaining competitive advantage against imitation
Requirements for imitation: way to prevent imitation
Identification: obscure superior performance
Incentives for imitation: deterrence, pre-emption
Diagnosis: rely upon multiple sources of competitive advantage to create causal ambiguity
Resource acquisition: base competitive advantage upon resources and capabilities that are immobile and difficult to replicate

What are the stages of value chain cost analysis
Using the value chain for cost analysis
Stages of the analysis
- Identify the main value chain activities
- Identify the cost drivers at each stage of the value chain
- Allocate total costs between value chain activities
- Identify linkage between activities
- Identify opportunities for cost reduction
What are the ways for identifying differentiation potential using the demand side?
The product: what does it need to satisfy, what are the key attributes
The customer
- How do they choose: relate patterns of customer preference to product attributes, price premiums
- What motivates them: demographic, sociological, psychological etc.
Formulate differentiation strategy:
Select product positioning relative to attributes
Select target customer group
Ensure customer product compatibility
Evaluate costs and benefits of differentiation

How do you identify the differentiation potential on the supply side?
Using the value chain to identify differentiation potential on the supply side

What are the advantages and disadvantages of outsourcing?
Advantages
- Potentially less expensive if process is used on an ad hoc basis
- Gain from outside expertise and competence
- Flexibility to cope with uncertain demand or to render cost base more variable
- Frees mgmt. up to focus on more important strategic issues
Disadvantage
- May be cheaper in house if the activity is perpetual and continuing
- Exposes firm to risk from poor quality or unreliable/unstable provider
- Loss of organisational learning and new knowledge creation
- Might nurture competitors who can learn and move up the value chain
What are the pros and cons of value chain analysis?
Pros
- Examines linkages between activities so that there is an increasing synergy between the activity systems (one activity enhances another to achieve its objectives)
- Ensure the ability to achieve consistency with standards and procedures (content created by one area is not destroyed by another)
- Helps build core competencies to differentiate with other providers
Cons
- Predominantly focussed on manufacturing type firms and hence how it would apply to services needs further development
- Firm focused which might need extending as firms become more networked through digital technologies
Explain how complex network structures are becoming more prevalent to complement and build resources and capabilities?
Coordinated value chains
Linked processes
Shared data
Combination of
- Outsourcing
- Partnerships
- Alliances

If network effects are important, what are the two sources of value?
If network effects are important value may have two roots
Greater product value
Consumers value the product because it is intrinsically valuable to them
What would this be worth to me if I were the only buyer in the world?
Network value
Consumers value the product because of the size of the network
How many other people are likely to buy this product?
What are the two sources of network effects?
There are two sources of network effects
Direct network effects
Network size
Value increases with the number of other individuals who own the same product
E.g. telephones, fax machines, Facebook
Indirect network effects
Complementary products/services
Value increases with the number of complementary products that are available
E.g. videogames, software, VHS/Beta
Explain why markets tip
In some markets network effects are so important that when the market develops a preference for one product or standard the whole market will “tip” to that product.
Once the market tips, it’s very hard to regain market share. It’s even harder to introduce a new, competing standard.

What is a standard?
A standard is a specification that allows for interoperability
E.g.
Cups and lids
Pistons and engines
Telephones and jacks
Explain how strong network effects and high switching costs may create “lock-in”
- All consumers might prefer to adopt a different standard
- But, if it is expensive to switch between standards and network effects are important and costly to create, then markets may become “locked in” to particular standards
- Lock in has dramatic competitive implications
- Competing on standards driven markets
- Establishing and exploiting standards
- Standards ‘win’ when a critical mass of consumers have adopted them
- When a critical mass of key players believe that the standard will be adopted
- Establishing and exploiting standards
EXAMPLES: NINTENDO AND SEGA, US TV
How can a firm promote adoption of its standard?
The sheer power of the concept, design or delivery of the product
Coming to market ahead of competition
Building expectations
Developing or encouraging the development of, complementary products and services (Facebook, Apple Ipod)
Very aggressive pricing: “giving the product away”


