Lecture 11 Flashcards
(57 cards)

Paramphistomosis
Where do Paramphistomosis locate
Immature - duodenum/abomasum
Mature - rumen and reticulum
- Wha the intermediate host of Paramphistomosis
Snails from Planorbidae
What is the distribution of Paramphistomosis
Depends on the presence of the planorbid snail
How are animals infected with Paramphistomosis
Ingestions of grass with metacercaria
- During rainy season
- During dry ceason - snails take refuge in marshy areas
Who is susceptible ot Paramphistomosis
Weaner cattle and lambs
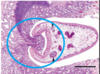
What is the pathogenesis of the immature stages of Paramphistomosis
- Locate in the wall of the duodenum and the abomasum
What do the immature stages feed on Paramphistomosis
Mainly tissue but also blood
What damage do the immature stages of Paramphistomosis cause
- Mechanic action/trauma by posterior sucker and movement
- Erosion of the intestinal villi
- Antigenic activity -> acute inflammatory reaction
What do the immature stages of Paramphistomosis cause
- Congestion and oedematous enteritis
- Erosions and petechiae surrounded by necrotic zone
- Atrophy of the villi
Paramphistomosis
Where do the mature stages loacte of Paramphistomosis
- In the rumen and reticulum

Paramphistomosis
What are the clinucal sings with Paramphistomosis
- Heavy infection with immature parasites -> have clinical signs
- Usually cilincal signs are seen on young animals
- With immature parasites clinical signs can develop in 2-4 weeks
- Anorexia, polydipsia, weight loss, fluid, foul smelling diarrhoea
- Dehydration, weakness, anaemia, submundibular, oedema, death
- Moderate infections will havr reduced weight gains or milk production or ill thrift
How to diagnose Paramphistomosis
- History
- CS
- Coproscopy: infection with immature parasites
- Microscopic exam: NEGATIVE ( due to them being immature forms so they dont lay eggs)
- Macroscopic exam: immature stages gan be fround in poo
- Microscopic ecam: positive - sedimentation method
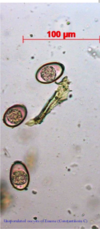
What do the eggs of Paramphistomosis look like
Ovoid with unequal poles, pale or geenish, smooth and thin shelled with an operculule at one end

Paramphistomosis
Treatment for Paramphistomosis
- Oxyclozanide
- Niclosamide
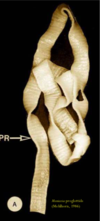
Moniezia expansa
Explain the morphology of Moniezia spp
- 4 suckers, no rostellum
- 3-5m long and ip to 2cm wide

Moniezia
Moniezia