Lecture 4: Hearing and the Vestibular Senses Flashcards
(42 cards)
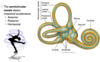
The scala vestibuli and scala tympani are continous, fluid-filled compartments which contain?
Perilymph
Perilymph is most similar to what kind of fluid and what is its ion content like?
- Most similar to ECF
- High in [Na+] and low [K+]

Where is Endolymph found, what is it most similar to, and what is its ions concentrations like?
- Found in the Scala Media
- Most similar to ICF
- High in [K+] and low in [Na+]

What creates the chamber (scala media) that is isolated from the periymph?
The Basilar and Reissner’s membrane

The composition of the _____ will have a significant effect on the transduction of sound waves into actions potentials?
- Endolymph
- Large electrical gradient (scala media has high positive charge)
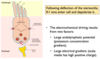
What components of the ear transmit and amplify the sound waves from the tympanic membrane to the oval window of the cochlea?
The ossicles

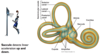
High frequency (short wavelength) sounds cause the maximum vibration of the basilar membrane where?
Closest to the oval window

Low frequency (long wavelength) sounds cause the maximum vibration of the basilar membrane where?
Farthest away from the oval window (towards to helicotrema)

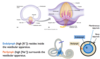
Hair cells of the ear are what kind of receptors and convert what kind of energy?
- Mechanoreceptors
- Convert mechanical signal to an electric signal

What is each hair cell composed of that increase in length; what are they connected to and the function?
- Composed of distinct arrangement of shorter sterocilia that increase in length
- Each stereocilia connected to another at the top by an extracellular filamentous protein, known as the tip link
- This links the stereocilia together, allowing for deflection as a bundle

During transduction, if the stereocilia are bent towards the kinocilium (tallest stereocilia) what occurs?
- K+ ions enter the hair cell
- Hair cell depolarizes and opens voltage-gated Ca2+ channels
- Incoming Ca2+ leads to release of glutamate from synaptic vesicles

During transduction, if the stereocilia are bent away from the kinocilium (tallest stereocilia) what occurs to the hair cell?
Hair cell hyperpolarizes

Deflection of the stereocilia causing depolarization also causes the release of what NT and generates what?
- Release of glutamate
- Generation of AP’s in 8th nerve fibers

Which hair cells are primary source of auditory information and which act as an amplifier?
- One row of inner hair cells = primary source of auditory info
- Three rows of outer hair cells = acts as an amplifier

Hair cells have both afferent and efferent innervation, what type of afferents are the inner hair cells vs. outer hair cells?
- Inner hair cells = type I afferents
- Outer hair cells = type II afferents

The Dorsal (posterior) cochlear nuclei is involved in what process of hearing?
Integrates the acoustic information with somatosensory information for localizing sound (i.e., where the sound is)

The Ventral (anterior) cochlear nuclei is involved in what functions of hearing?
- Begins processing the temporal and spectral features of the sound (i.e., what the sound is)
- Identifying the nature of the sound (i.e., is it someones voice telling me to get out of the way or a car horn)

What is the first site in the brainstem where information from both ears converges; composed of what 2 primary nuclei?
- Superior Olivary Complex
- Medial superior olivary nucleus
- Lateral superior olivary nucleus

What is the function of the medial superior olivary nucleus of the superior olivary complex?
- Generates a map of the interaural TIME differences, which helps localize the location of the sound
- Assuming that most times sound arrives in each ear at different times and microseconds matter!

What is the function of the lateral superior olivary nucleus of the superior olivary complex?
Generates a map of the interaural INTENSITY differences, which helps localize the source of ths sound

What is the function of the inferior colliculus in the localization of sound?
Suppresses information related to echoes, which would interfere with localization and arrives at a final estimation of localization of sound along the horizon

What is the function of the superior colliculus in the localization of sound?
Takes the location data from the inferior colliculus and adds the final dimension (vertical height) to create a spatial map of the sound’s location

The primary auditory cortex (A1) has a tonotopic representation of sounds, which areas are activated by LOW frequency and which are activated by HIGH frequency sounds?
- More rostral (superficial) areas are activated by LOW frequencies
- More caudal (deep) areas respond to HIGH frequencies
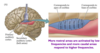
The primary auditory cortex (A1) is essential in conscious perception of sound and what other chacteristics of sound map to areas of A1?
- Loudness
- Modulations in volume
- Rate of frequency modulation
- More pure tones