Metabolic Diseases Flashcards
(69 cards)
Hemolytic Anemia
Premature Destruction of RBC
Caused by
- inherited defect - spherocytosis
- Hemoglobinopathies - thalassemia, sickle cell
- Nutrient Deficiency - iron, folate (B9), vit B12
- Infection
Tarui Disease (GSD VII)
Deficiency in PFK-1 (rate-limiting step in glycoysis)

Deficiency in PFK-1
Tarui Disease

F-1,6-BP Deficiency
Causes similar issues similar to Tarui disease, creates issues with producing glucose from gluconeogenesis

Von Gierks Disease (GSD1a)
Deficiency in Glucose-6-phosphatase (takes the phosphate off of G-6-P)
Unable to release glucose back into the blood stream from gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis
Deficiency of Glucose-6-phosphatase
Von Gierke’s Disease
Unable to free Glucose-6-phosphate
Fanconi-Bickel Syndrome
Mutation of GLUT 2 transport
Found in liver, pancreatis B cells, enterocytes, and renal tubular
Unable to take up glucose, fructose, and galactose
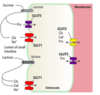
Mutation in GLUT 2
Fanconi-Bickel Syndrome
Unable to take up glucose, fructose, or galactose

Sorbitol Accumulation
Lack of sorbitol dehydrogenase
Sorbitol can not be converted to fructose
Causes swelling due to the osmotic ability of sorbitol
Hallmarked usually by cataracts

Hereditary fructose intolerance
Dysfunction of of Aldose B (found on liver)
Fructose is able to bypass the first 3 steps of glycolysis but requires Aldose B

Galactokinase Deficiency
Can’t phosphorylate Galactose into Galactose-1-P
Causes a built up galactitol and galactose in the blood and urine
Causes cataracts

Classic Galactosemia
Dysfunction in GALT
GALT is the rate-limiting step in conversion of galactose to glucose
Causes back-up and creates galactitol

Deficiency in GALT
Causes Classic Galactosemia

GSD0
Deficiency in glycogen synthase
Patients can’t make glycogen
Glycogen Synthase Deficiency
GSD 0
Cori Disease/GSD III
Deficiency in alpha-1,6-glucosidease
Debranching enzyme
Results in a large number of short branch glycogen
Deficiency of Alpha-1,6-glucosidase
Cori Disease
Inability to make glycogen branches
Andersen Disease/ GSD IV
Deficiency in glucosyl (4:6) transferase
Many long chain glycogen with fewer branches
Deficiency of glucosyl (4:6) transferase
Andersen Disease
Branching enzyme
McArdle Disease/ GSD V
Deficiency in muscle glycogen phosphorylase
Glycogen phosphorylase (rate-limiting step of glycogen breakdown)
Unable to supply muscles with enough glucose
Muscle Glycogen Phosphorylase Deficiency
McArdle Disease
Inability to break down glycogen
Hers Disease/ GSD VI
Deficiency of liver glycogen phosphorylase
Can’t break down in liver
Inability to control blood sugar
Causes hepatomegaly
Deficiency in Liver Glycogen Phosphorylase
Hers Disease/GSD VI
Pompe Disease/GSD II
Defect in acid maltase (alpha-glucosidase)
Used in lysosomal glycogen degradatoin pathway
Glycogen accumulates in lysosomes
ERT (enzyme replacement treatment)