Midterm Flashcards
(164 cards)
World Cultural Realms

Functional region
a region marked less by it’s sameness than it’s dynamic structure
- a spatial system focused on a central core
- A region formed by a set of places and their practical integration
(also known as nodal region)
Relative Location
In relation to something else, ex: “he’s closer to the desk than me”; qualitative
Convergent Lift

Biosphere
Atmosphere, lithosphere and lithosphere combined
- Resources (opportunities) vs. Tolerance (constraints)
- Biogeography
- studies the geographic distribution of living organisms
Biomes
global scale ecosystem classification sceheme (climates, soil etc.)
Transition Zone
- An area of spatial change where the peripheries of two adjacent realms or regions with
- marked gradual shift (rather than a sharp break)
Map
A 2-D representation of the Earth’s surface that is:
- Projected
- Reduced
- Generalized
- Explained
- Concept of ________ is inseperable from location
- Aid in understanding of patterns in space
- Visual means of communications of these relationships
Third World
Everyone Else. (Not Economically stable, not fitting into 2nd world because it’s less devel.)
First World
West. Europe, USA + Canada, New Zealand, South Korea, Japan
Equal Area Map
Area is preserved in this type of projection
Periphery vs. Core
_________ ex: Farms
__________ ex: Downtown
______ supports the _________
Conformal Map
Shape is preserved in this map projection
Absolute location
Quantitative (number attached) ex: “he is 10 metres from the desk”
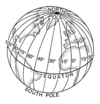
- Graticule
- Latitude + Longitude
Thematic map
based on a topic/theme
Line scale

What are some concepts in Human Geography?
Location, distribution, process + interrelationships
What is a Natural Landscape?
the original landscape that exists before it is acted upon by human culture
Culture VS Environment
The environement does not control culture and innovation
Reaction to opportunities and constraints, people are the deciding factors not environements
Peters Projection

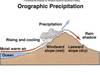
Stream discharge possible factors
- Climate
- Precipitation (amount and timing)
- Temperature (evaporation + seasonality)
- Vegetation
- Geology
- Bedrock (porosity permeability)
- Groundwater
Generalized map characteristics
- Detail through simplification, selection, combintion or smoothhing
- May be a result of necessity (i.e. scale reduction)
- May be the mapmakers choice (i.e. information converged)
Realm
the result of interaction between human societies and natural elements
geographic _________ change over time
clusters of humans
Koppen Climate System