MRI and CT Flashcards
(28 cards)
- What are the arrows pointing at?

1.
Quadriceps/patella tendon/patellla lig
Infrapatellar fat pad
PCL
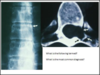
- What are the arrows pointing at?
- What level is this at?
- What is A?

- Osteophytes from lig flavum
- L5, S1 (disc because no homogenous white in VB)
- Lig flavum
- What is the approximate level
- Describe the main radiological feature
- Give 2 possible diagnosis

- C2 (dens, no clean shape to trachea/pharynx)
- Missing part of the pars
- GCT, ABC, osteoblastoma
- Which lines of alignment would be more appropriate on the following films?

1.
COG
ALL, PLL, SLL
ADI
Ruth jackson
Cx curve angle
- Describe what is the arrow pointing at?
- What condition is this commonly associated with?
- List 4 other common radiographic findings of AS
- What is the common type of patient with this condition?
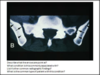
- Rosary bead formation of iliac side of SIJ
- AS
- Dagger sign, trolley tracks, shiny corner sign
- Young males, 15-25yoa
- What structure is the crossed arrow pointing at?
- What can this structure create the formation of?
- List some common symptoms of spinal cord compression

- Lig flavum
- Osteophytes
- Mimics claudication, tiredness, fatigue, numbness and tingling, muscle weakness and hypertonia, increased reflexes, fasciculations
What are the 3 tissues commonly responsible for causing spinal pain?
What nerve roots do the blue boxes correlate with?

1:
Disc - posterior annulus or nucleus
PLL, lig flavum (can cause osteophytes)
Facets
2: L5 disc space you see L5 nerve root exiting and S1 is about to leave. So blue boxes = S1
- What is the view and the type of study?
- Label A and B
- What is occurring at C
- What might cause this?

- MRI Fat sat coronal
2.
A - Supraspinatus
B - Trapezius or deltoid (most likely trapezius)
- Inflammation, bleeding
4.
- Labral tear (bankart lesion)
- Hillsacs lesion
- Describe the prominent radiographical findings?
- What is the diagnosis
- What are A B and C

- Non union (?) of the neural arch
- Spina bifida occulta
3.
A = Semispinalis, spinalis
B = Psoas
C = QL
Provide at least 6 muscles that may be effected from irritation of the S1 nerve root

- gluteus maximus muscle
- gluteus medius muscle
- gluteus minimus muscle
- tensor fasciae latae
- piriformis
- obturator internus muscle
- inferior gemellus
- superior gemellus
- quadratus femoris
- semitendinosus
- gastrocnemius
- flexor hallucis longus
- abductor digiti minimi
- quadratus plantae
What is a MIPS study?
What bony finding can we see in this image
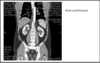
Maximum intensity projection study
Shows viscera and great vessels
- We can see an L1#
- Describe the prominent radiological findings
- What would be the diagnosis
- How common is this finding?

- Osteopaenia, discrete areas of sclerosis in the ilium bilat
- Mets
- ..??
- What is this view?
- Looking at the femoral heads; what is the major finding?
- What might result in this finding

- An MRI T1 weighted coronal
- Hypointensity in the right femoralhead
- Avascular necrosis, infection, tumour
- What is this type of image (full description)
- Describe 4 radiographic findings
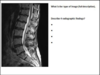
- MRI T2 sagital of the Lx region
2.
- Anterolithesis of sacral base
- Disc bulges at L4/5, T12/L1 and L1/L2
- Blood vessels (posterior VB)
- Schmorls nodes
- Decreased joint space
- Hyperintense local region in sacal base
- Anterior osteophytic projections L1,2,3
Image C is a type 1 MRI and image D is a type 2. Given this info, give an diagnosis for the pictures to the right and explain your answer

Osteomyelitis - water predominant content within the VB’s
Avascular necrosis - high water content
Mets
What is the type of study?
- Provide the correct description of the radiographic findings
- Limitation?
- Sensory changes - dermatomal
CT Bone window axial with contrast (myelogram)
- Left paracentral posterolateral disc herniation impingement/displacement of the S1 nerve root
- Myograms only show inside the spinal canal
- Potential S1 (achilles) reflex changes, posterior leg and lateral foot dermatome, myotome is peroneus longus and brevis
- What are the 2 arrows pointing at?
- Provide 2 radiographic findings

- Gastrocs and hamstrings tendon - semimem, semiten or biceps femoris
2.
Variscosities
Anterior and posterior meniscal horn tears
- Given this is the L4/5 disc space, what nerve will be affected
- What are the major muscular innervations of this nerve?

- The exiting nerve root the L5 nerve root
2.
- gluteus maximus muscle mainly S1
- gluteus medius muscle
- gluteus minimus muscle
- tensor fasciae latae
- tibialis anterior
- tibialis posterior
- extensor digitorum brevis
- extensor hallucis longus
- hamstrings
- List the two types of images seen
- What is a scout film

- Axial CT ST (top) and bone window (bottom)
2.
- Describe any radiographic findings
- What level is this?

- Left transverse foramen stenosis
Osteophytes as a result of PLL
- C3-C6 - the trachea is nice and round
- What are the major findings for each of the letters
- Which reflex might be affected in this patient

1.
A - Right common iliac artery
B - Psoas major
C - L4 nerve root (exiting)
D - Subcutaneous tissue
E - Inferior vena cava
F - Facet joint
2.
Patella reflex
- What is the CT showing?
- DDx

- an aggressive geographic lesion
2.
Mets/primary neoplasm
Infection (Supp OM)
Bone Cyst
- What would the following be termed?
- Is it clinically significant

- Costochondral calcification
- No, most people would have a little bit of it, esp above 40