MSCT Week 5: Papulosquamous Skin Eruptions Flashcards
(73 cards)
Papulo means in papulosquamous eruptions
Plaque - raised skin lesion with epidermal component
Squamous in papulosquamous means
scale or excess shedding of keratinocytes
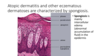
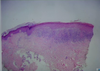
Pathology?


Pathology?

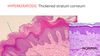
Hyperkeratosis is?
Thickened Stratum Corneum
Parakeratosis is?
Presence of keratinocytic nuclei in the stratum corneum
Acanthosis is?
Thickened spinous layer also known as epidermal hyperplasia
Acanthosis AKA?
Epidermal Hyperplasia
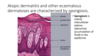
Pathology?


Descriptions
Pathology?

- Acanthosis
- Hyperkeratosis
- Parakeratosis
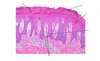
Pathology?

Acanthosis
Hyperkeratosis
cant see Parakeratosis
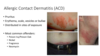
Pathology?
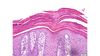
- Hyperkeratosis
- Parakeratosis
- Neutrophils in the stratum corneum
Pathology?
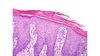
Hyperkeratosis
Parakeratosis
acanthosis might be hard to see from this magnification
neutrophils in the stratum corneum
What is Psoriasis?
A chronic, inflammatory skin condition
Psoriasis prevalence?
- 2% of the US population
- can be seen at any age, peaks in diagnosis in early 20s and middle age
Psoriasis Risk Factors
Strong genetic component (1/3 have affected 1st degree family)
Psoriasis Characteristics
2 listed
- Waxes & Wanes but has a chronic tendency
- May or may not be itchy
Psoriasis Characteristics Overview

Psoriasis Age of Onset
can be seen at any age, peaks in diagnosis in early 20s and middle age
Psoriasis Morphologies
8 listed
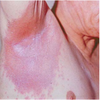
Plaque
Guttate
Inverse/Flexural
Generalized/Erythrodermic
Pustular
Acral/Palmoplantar
Auspitz Sign = pinpoint bleeding in dermis when scale removed
Clinical pearl: Nail Pitting

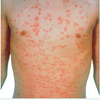
Guttate Psoriasis
Having drops or droplike markings
Inverse/Flexural Psoriasis appears where on the body?
in the skin folds like arm pits
Psoriasis type?
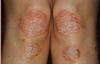
Plaque