MSK 4 - Upper Limbs 4 Flashcards
(77 cards)
What are the 3 functional groups that the muscles of the posterior forearm can be organised into?
1) Muscles that extend and abduct or adduct the hand at the wrist joint
2) Muscles that extend the medial four digits
3) Muscles that extend or abduct the thumb
What is A?

Olecranon
What is B?
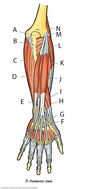
Anconeus
What is C?

Flexor carpi ularnis
What is D?

Extensor carpi ulnaris
What is E?

Extensor digiti minimi
What is F?

Extensor pollicis longus
What is G?

Anatomical snuff box
What is H?

Extensor pollicis brevis
What is I?

Abductor pollicis longus
What is J?

Extensor digitorum
What is K?

Extensor carpi radialis brevis
What is L?

Extensor carpi radialis longus
What is M?

Lateral epicondyle
What is N

Brachioradialis
What is the action of extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis on the wrist joint?
They both extend and abduct the wrist joint.
Other than extension and abduction of the wrist, what other actions are the extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis involved in with the help of the flexor carpi radialis?
They cause radial deviation of the wrist
What are the muscles that extend the medial 4 digits?
- Extensor digitorum
- Extensor indicis
- Extensor digiti minimi
What is the origin of the extensor digitorum?
Lateral epicondyle of humerus
How many tendons does the extensor digitorum have?
As its fleshy muscle belly runs distally it ducks under the extensor retinaculum, and divides into 4 tendons for the fingers – very similar to FDS and FDP in Lesson 3.
What is A?

Abductor pollicis longus
What is B?

Extensor pollicis longus
What is C?

Extensor pollicis brevis
Where is the supinator found?
This muscle envelops the neck and the proximal part of the shaft of the radius, covering it completely, except on its medial side.

















