MSK cadavers upper limb Flashcards
(56 cards)


What is the common flexor origin in the forearm for superficial & intermediate flexors
medial epicondyl of humerus
what is the innervation of the superficial flexors
the superficial flexors are innervated by the median nerve (FCR, palmaris longud and pronator teres), apart from flexor carpi ulnaris- ulnar nerve
muscle in the intermediate flexor compartment of forearm & its innervation
flexor digitorum superficialis
Median nerve


A. Flexor carpi ulnaris
B. Palmaris longus
C. Flexor carpi radialis
D. Pronator teres
Action & innervation of brachioradialis

Flexion of the elbow
Innervation = radial nerve
label deep group of anterior forearm muscles & their innervation

FDP- lateral half= median n
medial half= ulnar n
FPL- median n
Pronator quadratus- median n
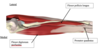
inserion and origin for FDS and FDP
FDS=Palmar surfaces of middle phalanges of medial 4 digits
FDP= Palmar surface of distal phalanges of medial 4 digits
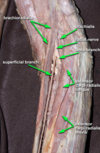
neurovascular structures of the forearm


Describe Allens test
To determine the patency of the arteries in the distal forearm (prior to sampling of arterial blood, or insertion of arterial lines), Allen’s test is used.
The reason that this is performed is because in some individuals a unilateral circulation exists in the distal forearm. Therefore, if any cannulation is performed there is a risk of causing ischaemia (due to reduced blood flow) to the hand
Contens of the anticubital fossa from lateral to medial
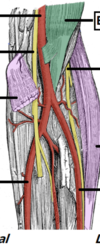
Radial nerve, Brachial tendon, Brachial artery, Median nerve
Really Need Beer, To Be At My Nicest

What 4 carpal bones does the flecor retinaculum anchor to
scaphoid, trapezium, hamate and pisiform
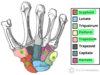
Name the contents of the carpal tunnel & label diagram

Contents of Carpal Tunnel
4 tendons of flexor digitorum profundus
4 tendons of flexor digitorum superficialis
1 tendon of flexor pollicis longus
Median Nerve


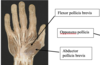
what are the four mucles in the deep part of the central component of the palm
- Flexor digitorum superficialis
- Flexor digitorum profundus
- Flexor tendon sheaths: flexor pollicus longus
- lumbricles
what is the function of the lumbricals
flex the fingers at the metacarpophalangeal joints and extend the interphalangeal joint of 2nd to 5th digits.
- bend a straightened finger
what do the lumbricals arise from
Medial and lateral aspects of the FDP tendon, between the 1st to 5th metacarpals
label this diagram

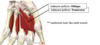








label these