Nasal Cavity & Ear II Flashcards
(69 cards)
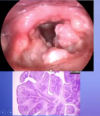
What aspect of the provided images indicate a diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma

Left: keratin pearl
Right: Intercellular bridges
What are the major risk factors for squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck?
- Chronic smoking / alcohol use
- Sunlight & pipe smoking
- HPV 16 (oropharyngeal cancer)
What is the difference in prognosis for squamous cell carcinoma that is HPV (+) vs. HPV (-)?
HPV 16 (+) have greater long-term survival
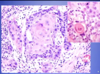
What pathology is shown in the provided image?
What features of the photos indicate this diagnosis?

Squamous cell carcinoma
L: ulceration & induration of the oral mucosa
R: malignant keratinocytes invading underlying connective tissue stroma & skeletal muscle
What pathology is shown in the provided image?

Verrucous carcinoma
“wart-like” filiform appearance
don’t tend to metastasize but can cause problems where they are
What is a detigerous cyst?
Treatment?
Cyst originating around the crown of an unerupted tooth
Complete remoal of the lesion is curative

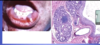
What pathology is shown in the provided image?
Describe how it was identified.

Unilocular lesion most often associated with impacted 3rd molar (wisdom) teeth
What is a periapical cyst?
Treatment?
Cyst inflammatory in origin found at the apex of the tooth
removal fo the offending material
What pathology is shown in the provided image?

periapical cyst
What is a keratocystic odontogenic tumor?
Most commonly affected demographic?
Treatment?
Radiographically present as well-defined unilocular/multilocular radiolucencies posterior to mandible most common
10-40, males
complete removal of the lesion
What pathology is shown in the provided image?
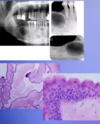
Keratocystic odontogenic tumor
locally aggressive
Multiple keratocystic odontogenic tumors is associated with what syndrome?
It is associated with what mutation?
Nevoid basal cell carcinoma
PTCH gene mutation
What is an odontoma composed of?
hamartoma
enamel, dentin, +/- cementum & varying number of tooth-like elements
What is shown in the provided image?

Odontoma
What are the features of an ameloblastoma?
benign, but locally aggressive with high recurrence rate
expansile, multiloculated “soap bubble” appearance
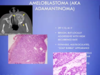
What patholgoy is shown in the provided images?
Describe the featues of each

Radiographically: “soap bubble”
Histologically : stellate reticulum, peripheral palisating (outside perpendicular to inside cells) with apical clear cytoplasm
What are the common causes of laryngitis?
allergic, viral, bacterial or chemical (tobacco smoke)
gastroesophageal reflux
systemic infections (tuberculosis & diptheria)
What is the cause of laryngotracheobronchitis?
Presentation?
“croup” in children - parainfluenzavirus
nonspecific respiratory symptoms & low grade fever
w/in 1-2 days hoarseness, barking cough & inspiratory stirdor
What are the common causes of laryngoepiglottis?
Presentation?
H. influenza, RSV, N. meningitidis, Strep
Medical Emergency in children
Cherry red epiglottis, drooling , tripod posture
What is reinke’s edema?
severe swelling of the vocal cords that occurs in heavy smokers
change in character of the voice & progressive hoarsness
What are singer’s nodules?
reactive nodules that occur in people who put great strain on their vocal cords
change in character of voice & progressive hoarsness
What can happen to individuals who put put great strain on their coval cords or have reflux irritation?
contact ulcers
change in character of the voice & progressive hoarsness
What pathology is shown in the provided image?

Singer’s nodule
What patholoyg is shown in the provided image?

Reinke’s edema