Neuromuscular Junction Flashcards
(30 cards)
Which of the following terms refers to a chain of sarcomeres?
Muscle
myofiber
myofibril
Myofilament
Myofibril
Which of the following sarcomeric bands does not undergo a change in length during the contraction of a skeletal muscle?
A band
H band
I band
J band
A band
Which of the following sarcomeric bands is composed entirely of actin filaments
A band
H band
I band
J band
I band
Dihydrophyridine(DHP) channels are part of which of the follwing strucutres?
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Plasmalemma
T tubules
Z discs
T tubules
Ryanodine sensitive calcium ion release channels are part of which of the following strucutures?
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Plasmalemma
T tubules
Z discs
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Which of the following sarcomeric bands is composed entirely of actin filaments?
A band
H band
I band
J band
I band
Which of the following events occurs first during the transmission of a signal from an alpha motor neuron to a skeletal muscle fiber?
End plate depolarization(EPP)
Caclium ion influx into axon terminal
Exocytosis of synaptic vesicles
Sarolemma action potential
Calcium ion influx into axon terminal
Which of the following represents the factor by which the concentration of calcium ion increase in the cytosol after relase from the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
10
50
100
1000
100
Which of the following maintains an optiumum calcium concentration gradient to facilitate return of calcium to SR?
Calsequestrin
SERCA
DHP
Ryanodine
Calsequestrin
Fast twitch fibers have which of the following charecteristics
- They are reddish in color compared to slow twitch fibers
- They have more mitochondria than slow twitch fibers
- They have more myoglobind than slow twitch fibers
- they are more fatigueable than slow twitch fibers
They are more fatigued than slow twitch fibers
Which of hte following represents an example of an eccentric contraction?
- Triceps muscle during the throwing ball
- Triceps muscle while raising the body from the floor udring a push up
- Triceps msucle while lowering the body to the floor during a push up
- Biceps muscle while raising the body during a pull-up
Tricep muscle while lowering the body to the floor during a push up
Which of the following are anchored to the presynaptic membrane and associated with synaptic vessivles to which they are tethered by short filaments?
Synaptic vesicles
Calcium channels
Dense Bars
Dihydropyridine channels
Dense bars
What are charecteristics of a single axon terminal?
- Many mitochondria
- Synaptic vesicles with acetycholine:
- Release neurotransmitters via exocytosis:
- 300,000
- Release neurotransmitters via exocytosis:
- Dense bars:
- Anchored to the presynaptic membrane and associated with synaptic vesicles to which they are tethered by short filaments
Synaptic gutter(trough) related to the charecteristics of a single axon termin
- This is a groove or furrow in the surface of a sarcolemma in which the axon terminal makes contact with the acrolemma
- Subneural clefts are smaller clefts or troughs in the bottom of the synaptic trough
Synaptic Cleft
- 20-30nm wide
- This is a very narrow but real gap between the axolemma of the axon terminal and sarcolemma of the innervated muscle fiber
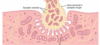
In order for an acetylcholoine gated ion channel toopen how many Ach molecules are necessary to attach to its alpha subunit?
One
Two
Three
Four
Two
Sarcolemma of hte skeletal muscle related to the charecteristics of a single axon terminal
- Has acetylcholine gated ion channels:
- 275,000mw
- 2 a proteins, 1 b protein, 1 y protein , 1 sigma protein
- Tubular channel remains closed until two acetylcholine molecules attach to its a subunits
- Acetylcholinesterase
Which of hte following represents the first thing that happens after Ach binds to the ligand gated channels on the sarcolemma
An end plate potential is created on the muscle fiber
- if end potential is strong enough there are nearby voltage gated channels that will open, and create a potential and must get up to threshold for potential to happen
Vesicles for acethychole are transport to the axon terminal from where
Rough ER
Smooth ER
axon terminal membrane
Golgi
- Golgi
How are action potentials communicate to other cells?
- vesicles formed in the golgi appartus and are carried by axonal transport to the axon terminus where they are filled with Ach
- Ach synthesized in the cytosol of the nerve axon terminal
- Action potential arrives at the terminus of the axon, voltage gated calcium channels open and calcium ions enter the axon terminus
- calcium ions are thought to draw synaptic vesicles closer to the nuerolemma next to the voltage gated calcium channels
- moves into the axon because calcium concentration is greater on the outside of hte cell
- calcium ions are thought to draw synaptic vesicles closer to the nuerolemma next to the voltage gated calcium channels
- `125 vesicle fuse to the nueronal membrane and empty their contents into the synaptic ceft
- 2 Ach molecules bind to each ligand gated channel on the sarcolemma
- Both Na and K ions pass thorugh the channels , but Na ions more permeable
- Principal effect is for large # of sodium ions to pass through the muscle fiber membrane(sarcolemma) creating the end-plate potential(50-75mV) which initiates an action potential on the sarcolemma

What happens to the action potential after it leaves the sarcolemma ?
- Action potential on the sarcolemma continues down the T tubules and activates voltage gated dihydropyridine chanels
- Dihydropyridine channels activate ryanodine receptors(ryanodine-sensitive calcium ion release channels) on sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes ,allowing calcium ions to move quickly through the ryanodine receptors into the cytosol at the A-I boundaries
- The ryanodine receptor is also activated by the calcium released into the cytosol thus allowing more calcium ion to be released
- Calcium ions bind to troponin in the sarcomeres, resulting in the sliding filament mechanism
- High cytosolic calcium ion concentrations(after calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum) promotes ryanodine channel closure

What happens after the action potential?
- Within a few seconds after each action potential clathrin coated pits appear in the axon nerve terminal. The pits separate from the plasmalemma and are then refilled as new synaptic vesicles
- Acetylcholine is removed from the synaptic cleft:
- Degradation into choline and acetate by acetylcholinesterase
- reuptake of choline by axon end terminal
- Diffusion of Ach away from site
What is meant by excitation contraction(electro mechanical) coupling?
- Electrical activity, once we get down to the pont we are releasing calcium from the cisternae
- we transformed to a mechanical stimulus
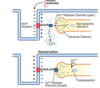
Explain the diagram
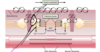
Excitation coupling in a muscle:(1) action potential causing release of calcium ions; (2) Reuptake of calcium ions


