Numerical Integration Flashcards
(34 cards)
What is the main question in this chapter?
How do we calculate integrals numerically?
What is a definite integral.
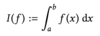
What is a quadrature formula?
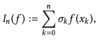
What are x0, …. xn and σ0, … ,σn in the following?
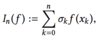
- x0, …. xn are a set of nodes
- σ0, … ,σn are a set of corresponding weights
What are the nodes also known as in the following?
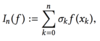
Quadrative points
What is the quadrature formula for the trapezium rule?
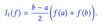
How can you derive quadrative formulas?
By integrating polynomials interpolants at equally spaced points.
What is the basic form of the interpolating polynomial in Lagrange form?

By integrating the following pn(x) what is the quadrative formula you get?
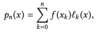

If the nodes are equidistant what is the following formula called?

Newton-Cotes formula
When is the Newton-Cotes formula called closed?
If x0=a and xn=b
Prove the trapezium with using the closed Newton-Cotes formula.
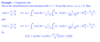
What is the theorem about the Newton-Cotes formula error bound?
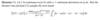
Prove the following theorem.
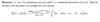
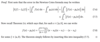
Why don’t Newton-Cotes formulae converge as n ➝ ∞?
Because they are based on polynomials interpolation at equally-spaced nodes
What is the idea with composite Newton-Cotes?
Divide [a,b] into m subintervals [xi-1,xi] of equal length h = (b-a)/h and use a N-C formula with small n on each interval.
What is the composite trapezium rule?
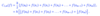
What is the overal error for the composite trapezium rule?

What is the trapezium rule exact for?
All lienar polynomials
Define degree of exactness.
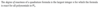
How do you check for degree of exactness?
Check the standard basis 1, x, x2, … ,xn
What is the Newton Cote’s formula for n=2 called?
Simpson’s rule
What is simpsons rule?
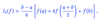
What is the main idea in Gaussina Quadrative?