Organic Chem :( Flashcards
(24 cards)
Esterfication and the equation
Esterfication is when an alcohol and a carboxylic acid react together in the prescence of a strong acid to form an ester. Many esters have their own distinctive fruit smell. This equation is in an equilibrium
Tertiary structure of Amino acid
It’s overall 3D shape that forms as a result of folding and bonding back on itself.various bonds such as disulfide bridges, hydrogen bonds, dipole-dipole, disperson forces and ionic bonds cause this to occur

Esters(-oate)

Alkenes(-ene)
Define Amino acid
Amino acids are the building blocks of protein
Oxidation of a primary alcohol
- Primary alcohol ->Aldehyde(limited Cr2O72-/H+ + cold)
- Aldehyde->Carboxylic acid(Cr2O72-/H+ + heat or MnO4-/H+)
- Primary alcohol->Carboxylic acid( MnO4-/H+ or XS Cr2O72-/H+ + heat)

Carboxylic acids (-oic)
B-pleated sheet
occur when sections of a-amino acid residues have small side chains. Such sections can fit closely alongside one another and become held together via hydrogen bonding
Condensation Polymerisation
The joining of individual monomers by the loss of small molecules: H20 or CO2
Oxidation of secondary alcohol
- Secondary alcohol->Ketone(Cr2O72-/H+ or MnO4-/H+)
Define structural isomers
Molecules that have the same molecular formula but have different chemical and physical properties
Define Polymer
Polymers are very large molecules composed of small repeating structural units
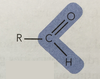
Aldehydes(-al)
a-helix structure:
Held in place by hydrogen bonds between a lone pair of electrons from the Oxygen atom of C=O, and the polar hydrogen atom of an N-H group four peptide links away
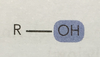
Alchols (-ol/hydroxyl-)
Secondary Structure of Amino acid
The regular arrangement of various sections of the protein chain.
- a-helix: a coiled section
- B-pleated sheets: corrugated structures
Define Primary structure of Amino acid
The specific sequence of individual a-amino acid residues. This is listed from the N-Terminus to the C-Terminus
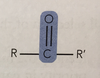
Ketones(-one)
Oxidation of tertiary alcohol
- Tertiary alcohol->No reaction

Amides(-amide)

Amines(-amine/amino-)
Metal and Alcohol Reaction
2R–OH(l) + 2Na(s) → H2(g) + 2R–O- + 2Na+
Esterfication decomposition reaction
Ester + H2O —>(H2SO4) carboxylic acid + alcohol
Alkene + Water —>(H2SO4) ????
Alkene + H20—>(H2SO4) Alcohol


