Paediatrics Haematology Flashcards
(125 cards)
What is haemoglobin made from?
4 protein subunits
Fetal haemoglobin (HbF) = two alpha and two gamma
Adult haemoglobin (HbA) = two alpha and two beta
Draw the oxygen dissociation curve for fetal and adult Hb?
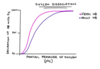
When does the production of HbF decrease?
From 32 to 36 weeks gestation (HbA is produced in greater quantities)
What is the problem in sickle cell disease?
Genetic abnormality for the beta subunit responsible for causing the sickle shape of the RBCs (doesn’t happen in fetal haemoglobin)
What is the treatment in sickle cell disease?
Hydroxycarbamide to increase production of fetal Hb
What is anaemia?
Low level of Hb in the blood (not a disease - the result of one)
What is haemoglobin?
Protein found in RBCs (iron is needed to make it)
What are the causes of anaemia in infancy?
Physiologic anaemia of infancy
Anaemia of prematurity
Blood loss
Haemolysis
Twin-twin transfusion
What are the causes of haemolysis in a neonate?
Haemolytic disease of the newborn
Hereditary spherocytosis
G6PD deficiency
When does physiologic anaemia of infancy occur and why?
At six to nine weeks of age in healthy term babies - high oxygen delivery to tissues caused by high Hb levels at birth cause negative feedback - production of erythropoietin by the kidneys is suppressed and there is reduced production of Hb by the bone marrow
Why do premature neonates become anaemic?
Less time in utero receiving iron from mother
RBC creation can’t keep up with rapid growth in first few weeks
Reduced erythropoietin levels
Blood tests remove a significant proportion of circulating volume
How to test for haemolytic disease of the newborn?
direct Coombs test (DCT)
What are the 2 main causes of anaemia in older children?
Iron deficiency anaemia secondary to dietary insufficiency
Blood loss from menstruation in older girls
What are the rarer causes of anaemia in children?
Sickle cell anaemia
Thalassaemia
Leukaemia
Hereditary spherocytosis
Hereditary eliptocytosis
Sideroblastic anaemia
What is a common cause of chronic anaemia and iron deficiency worldwide?
Helminth infection with roundworms, hookworms or whipworms
Can be very common in developing countries
What is the treatment of helminth infection?
Albendazole
Mebendazole
What are the causes of microcytic anaemia?
T – Thalassaemia
A – Anaemia of chronic disease
I – Iron deficiency anaemia
L – Lead poisoning
S – Sideroblastic anaemia
What are the causes of normocytic anaemia?
A – Acute blood loss
A – Anaemia of Chronic Disease
A – Aplastic Anaemia
H – Haemolytic Anaemia
H – Hypothyroidism
What are the two types of macrocytic anaemia?
Megaloblastic (result of impaired DNA synthesis preventing cell from dividing normally - vitamin deficiency)
Normoblastic
What are the causes of megaloblastic anaemia?
B12 deficiency
Folate deficiency
What is normoblastic macrocytic anaemia caused by?
Alcohol
Reticulocytosis (usually from haemolytic anaemia or blood loss)
Hypothyroidism
Liver disease
Drugs e.g. azathioprine
What are the symptoms of anaemia?
Tiredness
Shortness of breath
Headaches
Dizziness
Palpitations
Worsening of other conditions
What symptoms are specific to iron deficiency anaemia?
Pica - dietary cravings for abnormal things e.g. dirt
Hair loss - iron deficiency anaemia
What are some generic signs of anaemia?
Pale skin
Conjunctival pallor
Tachycardia
Raised resp rate



