PBL 1: Conception Flashcards
(114 cards)
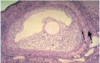
What makes up the ovaries histologically?
Medulla (in the centre)
Cortex (on the outside)
Capsule of simple cuboidal epithelium
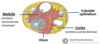
Describe the medulla of the ovary?
- This is the inner part of the ovary
- Comprised of stroma, containing the neurovascular stuctures (e.g. arteries, veins, nerves)

Describe the cortex of the ovary?
- Outer part of the ovary
- Composed of developing follicles (at various stages of development)

What kind of epithelium surrounds the ovaries?
Simple cuboidal epithelium
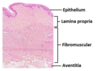
What are the four tunics of the uterine tube (from inner to outer layers)?
- Tunica mucosa (inner layer)
- Tunica submucosa
- Tunica muscularis
- Tunica serosa
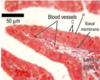
What part of the female reproductive tract is this histological image

The uterine tubes
Describe the structure of the tunica mucosa of the uterine tube?
- Highly folded around the length of the tube.
- Varies from different regions- ampulla is more elaborate folded.
- The isthmus is less elaborately folded
What are the sublayers of the tunica mucosa of the uterine tube?
Epithelium
Basement membrane
Lamina propria
What is the epithelium of the uterine tubes?
Simple columnar epithelium that has two different cell types.
Peg cells (also known as secretory cells).
Ciliated cells
What is the functions of the ciliated cells in the tunica mucosa layer of the uterine tube?
Beats in one direction (the direction towards the uterus)
Has two functions:
- Aids in the movement of the ovum from the ovary to the uterus
- Protects against infection but beating pathogens away from the uterus.
Describe the tunica muscularis layer of the uterine tube?
Consists of two layers:
- Circular layer of smooth muscle (inner layer)
- Longitudinal layer of smooth muscle (outer layer).
Thick layer of smooth muscle, which contracts to help move the sperm along the uterine tube.
Thickest in the isthmus- as this is the only part prior to the ampulla- where fertilsiation occurs
What kind of movement of the tubal musculature in the uterine tube helps move the sperm along the uterine tube to the ampulla?
Peristaltic movement i.e. progressive wavelike contractions
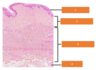
What are the 3 layers of the uterus?
- Endometrium (inner layer)
- Stratum functionalis
- Stratum basalis
- Myometrium (middle layer)
- Peritoneum (outer layer)

Name these layers of the uterus?
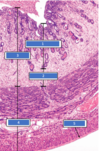

Compare the stratum functionalis and basalis?
Stratum functionalis
- Superficial layer
- Proliferates in response to oestrogen
- Becomes secretory in response to progesterone
- Shed during menstruation
- Blood supply is coiled arteries.
Stratum basalis:
- Deep layer
- More cellular
- Little to no change throughout the menstrual cycle
- Maintained during menstruation
- Blood supply is straight arteries.
NOTE: both contain uterine glands
The stratum functionalis becomes secretory in response to which hormone?
Progesterone
The stratum functionalis proliferates in response to which hormone?
Oestrogen
What is the blood supply to the stratum functionalis?
Coiled arteries
What is the blood supply to the stratum basalis?
Straight arteries
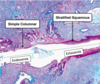
Describe the histology of the cervix region?
- The transition of epithelium occurs here.
- Two parts of the cervix:
- Endocervix
- Ectocervix
Compare the endocervix and ectocervix region?
Endocervix:
- Upper part of the cervix
- Lined by simpled columnar epithelium
- Contains mucous-secreting glands.
Ectocervix:
- Lower part of the cervix
- Lined by stratified squamous epithelium
The transition point between endocervix and ectocervix is called what?
External os
The endocervix is lined by which epithelium?
Simple columnar epithelium
The ectocervix is lined by which epithelium?
Stratified squamous epithelium