Pelvis 1 Flashcards
(41 cards)
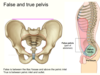
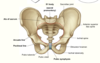
Where does the true pelvis exist? What is the false pelvis and what cavity is it apart of?
What is the shape of the pelvic inlet (males vs females)?
What is the shape of the pelvic outlet?
Inlet males: Heart shaped.
Females: Oval (for giving birth).
Pelvic outlet: Diamond shape.




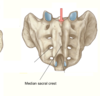

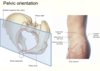
Explain the tilt of the pelvis
Pelvis actually lies in a tilted position.
In the coronal plane is the anterior supeior iliac spine and the pubic tubercle.
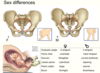
Female vs male sex differences in pelvis

Female subpubic angle is obtuse.
In males it is V shaped (angled).
Plus pelvic inlet differences.
The sacrum in female is straighter as well as coccyx, in males it can be more curved (more concave).
From supeior aspect in the females it is more cylcindrical shape and doesn’t taper (the pelvic space).
Male bony structures are bigger bc of heavier loads.
What are the 3 parts of the hip bone? How do they meet? When do they ossify?
Ileum (big one), Ischium and pubic bone.
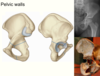
Join in a Y shape suture in ascetabulum.
Completes ossification 22 years old (ascetabulum).

Piriformis goes out via the greater trochanter to the greater trochanter of the femur.

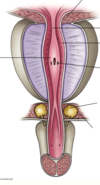
The two pelvid floor muscles: 1: _______ and 2: _________.
Muscle 1 can be split into 3: _________ , and 4: ________.
4: has different parts called _________ and ___________ / ____________.
1: Levator ani, 2: coccygeus (ischiococcygeus).
3: Illiococygeus, 4: pubococygeus.
called the puborectalis (not connected to the median raphe) and the pubovaginalis (which forms the sphincter of the vagina) /puboprostatis (wraps around the prostate).
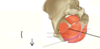
Pubococcygeus is separated further. Purple is the puborectalis, it does a turn around motion (doesn’t attach to median raphe), this helps with angulation between anus and rectum.
The part of the pubococcygeus part forms the pubovaginalis, this forms sphincter of vagina. In the males it goes around the prostate and is called the puboprostatis.
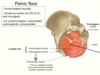
What are the pelvic floor muscles innervated by?
Branches of pudendal nerve (S2-S4) - external anal sphincter - inferior rectal branch of pudendal.


What are the two sections of the perineum (anterior and posterior)?
Urogenital triangle and anal triangle.

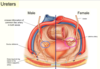
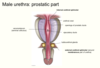
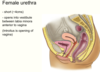
What are the contents of the pelvic cavity? (males vs females)


Rectovesical pouch in males.
Females: Vesicouterine and rectouterine pouch (pouch of Douglas).
Vesicle = relating to bladder.

Contents in the pelvis are ____peritoneal.
Infraperitoneal
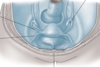
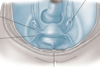


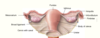
This is the ligamentous structures which the ovary is suspended, name the individual bits.
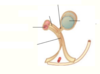



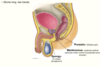
The bladder is _____ peritoneal.
The bladder is covered by the ____ muscle.
The smooth area of the bladder is called the ________. It has _ openings they are….
Retro.
Detrusor.
Trigone: 3 opennings, one for the internal urethral orifice, 2 for the ureteric orifaces.

Explain the nerve supply to the muscle of the bladder.
Nerve supply motor by the parasympathetic nerves via pelvic splancnic nerves.
Sympathetic supplies the internal urethral sphincter and trigone from L1 and L2, this is more important in males because before ejaculation these will be closed off so that there is no retrograde ejaculation.
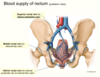
What is the blood supply to the bladder?
Lymphatics?
Blood supply comes from superior and inferior vesical artereis - branches of internal iliac.
Lymphatics follow artereis (internal and external iliac nodes).