Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Flashcards
(50 cards)
Bacterial Protein Synthesis
Prokaryotic ribosomes: 30s & 50s
- Transcription: DNA ⇒ RNA
- Translation:
- Aminoacyl-tRNA binds to 30s subunit
- Peptide bond formation and translocation on 50s subunit
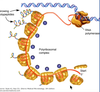
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
Sites of Action
-
30s ribosomal subunit
- Tetracyclines ⇒ ⊗ A-site
- Aminoglycosides ⇒ misreading of genetic code ⇒ insertion of incorrect AA
-
50s ribosomal subunit
- Macrolides & chloramphenicol ⇒ ⊗ peptidyl transferase
- Macrolides & clindamycin ⇒ ⊗ translocation of peptide from A-site to P-site

Resistance Mechanisms
-
Drug inactivation by bacterial enzymes
- Ex. ⊗ aminoglycosides or chloramphenicol
-
↓ Drug binding
- Ex. Aminoglycosides to 30s subunit
-
Active removal of drug by membrane proteins
- Ex. Macrolides
-
↓ Drug uptake
- Ex. Aminoglycosides via porins in bacterial membranes
Aminoglycosides
MOA
Binds 30s ribosomal subunit.
Causes irreversible misreading of the genetic code ⇒ insertion of incorrect AA
- Bactericidal
- Requires oxygen for uptake
- Ineffective against anaerobes

Aminoglycosides
Pharmacokinetics
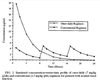
Concentration-dependent
- Effectiveness determined by ratio of peak concentration to MIC
-
Given as a single large daily dose
- Higher peak
- Lower trough (zero)
- Less monitoring
- Remains effective for 24 hrs even though serum concentration drops below MIC ⇒ Post-antibiotic effect
- Pharmacokinetic monitoring d/t potential for toxicity
Aminoglycosides
Pharmacodynamics
- Very low bioavailability
- Charged molecules ⇒ poor penetration into lung/sputum, bone, CNS, abscesses
- Do not penetrate tissues well ⇒ volume of distribution close to extracellular volumes
- Short half-lives
-
Eliminated unchanged primarily renally
- Dose adjustment for renal function
- Plasma concentrations monitored to minimize toxicity
Aminoglycosides
Adverse Effects
-
Dose-dependent nephrotoxicity
- Manifests as acute tubular necrosis or glomerular toxicity
- ↓ Renal function ⇒ ↑ [drug] ⇒ ↑ renal failure & ototoxicity
- Effect enhanced when given with other nephrotoxic agents
- Risk factors: age, hypovolemia, pre-existing renal dysfunction
- Important to monitor renal function and peak/trough serum drug conc.
-
Dose-related cochlear and vestibular toxicity
- Vestibular sx ⇒ dizziness, impaired vision, nystagmus, vertigo, N/V, poor postural balance, ataxia
- Cochlear sx ⇒ tinnitus, hearing impairment, irreversible deafness
- Often a delay in sx onset
-
Neuromuscular blockade
- Esp. in pts taking neuromuscular blockers or have myasthenia gravis
- Teratogenic

Aminoglycosides
Activity
-
Excellent activity
- Enterobacteriaceae
- Acinetobacter
- Pseudomonas
- Other GNR
-
Good activity when used in combo w/ cell-wall active agent
- Many GPC

Aminoglycosides
Clinical Uses
-
Combo w/ beta-lactam abx ⇒ serious gram-⊖ infections
- Febrile neutropenia
- Sepsis
- CF exacerbations
- Ventilator-associated PNA
-
Combo w/ beta-latam abx or vancomycin ⇒ serious gram-⊕ infections
- Endocarditis
- Risk of renal issues without the benefit of cure
- Osteomyelitis
- Sepsis
- Endocarditis
- Streptomycin ⇒ resistant TB
Aminoglycosides
Drugs

Tetracyclines
MOA
Binds to 16s rRNA of 30s ribosomal subunit.
Competitively blocks binding of tRNA to A-site.
Reversible ⇒ bacteriostatic activity

Tetracyclines
Pharmacodynamics
- High oral bioavailability
- Binds divalent and trivalent cations (Ca2+, Mg2+)
- ↓ absorption if ingested w/ milk or antacids
- Does not penetrate the CNS
-
Primarily eliminated renally
- Dose adjustment for renal insufficiency
-
Doxycycline ⇒ fecally eliminated
- No dose adjustments

Tetracyclines
Adverse Effects
-
Discoloration of developing teeth
- Contraindicated in pregnant women and children < 8 y/o
-
Esophageal irritation & GI upset
- N/V, borborygmus
- Should take drug with water while standing
- Photosensitivity

Tetracyclines
Drug Interactions
- Multivalent cations ⇒ chelation ⇒ ↓ absorption
- Cell-wall synthesis inhibitors ⇒ disruption of bactericial activity
Tetracyclines
Activity
- Atypicals
- Some MRSA
-
Strep. pneumoniae
- Resistance in many other Strep
-
Some GNR and GPC
- Limited by resistance
- B. burgdorferi
- H. pyloria
- Rickettsia
Tetracyclines
Resistance
Due mostly to efflux pump.
Tetracyclines
Clinical Uses
- Acne
- Uncomplicated CAP ⇒ doxycycline
- Tick-borne diseases ⇒ drug of choice
- PUD
- STI
- Malaria prophylaxis and treatment
Tetracyclines
Drugs

Tigecycline
MOA
Tetracycline derivative w/ expanded spectrum ⇒ same MOA
Binds 16s of 30s ribosomal subunit.
Competitively blocks binding of tRNA to A-site.
Reversible ⇒ bacteriostatic activity

Tigecycline
Pharmacodynamics
- Poor absorption
- Very large volume of distribution (Vd) ⇒ low plasma concentrations
- Long T½ but dosed q12h
- Hepatic elimination
Tigecycline
Adverse Effects
GI upset and N/V ⇒ 30% of pts
Tigecycline
Activity
Expanded spectrum vs Tetracyclines.
-
Many GNR and GPC
- Covers VRE and MRSA
- Good anaerobic coverage
- Does not cover Pseudomonas or Proteus species
Tigecycline
Clinical Uses
- Complicated polymicrobial infections
- Skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs)
- Intraabdominal infections
- Not adequate coverage for HAP
Macrolides
MOA
Binds to 23s rRNA of 50s ribosomal subunit
⊗ translocation and transpeptidase
Bacteriostatic