Protozoa - Flagellates Flashcards
(70 cards)
Flagellate cyst
Transmissive stage
Comes from asexual reproduction
Is a vegetative form resistant to unfavourable environment conditions outside of the host
Flagellate trophozoite
Parasitic stage
- active, feeding and motile
Flagellate Promastigote
Has a single anterior flagellum
Flagellate Amastigote
non-flagellated intracellular stage
Where does replication of Giardia occur?
In the intestine -> diarrhoea
How Giardia causes diarrhoea?
Disrupts absorption of nutrients -> malabsorption
- causes immune response
- extracellular parasite - sits on top of the hosts cells and absorbs glucose from the host
Significance of Giardia
Malabsorption and diarrhoea -> reduced growth and reduced cognitive development
Wheres vets come across Giardia?
In high populations desities - kennels
Day care centre
Farms (intensive)
Giardia zoonosis?
In waterborne outbreaks - Giardia cysts more susceptible to chlorination than Cryptosporidium oocysts
particularly from cattle
Lifecycle of Giardia
Cyst shed in faeces -> 24-48 hr for trophozoite to mature -> ingested -> into stomach -> pH changes, CO2 stimulates hatching -> trophozoite ready to go with flagella (suction cup to hold onto intestinal wall) -> asexual replication -> pushed further down GI tract OR immune system attacks it -> encystation process -> forms a cyst -> passed in faeces
Pathogenesis of Giardia
Villous atrophy and malabsorption via sheer bulk of numbers
immune response is to completely flush out GI tract -> Gi tract also loses mucous layer
-> IBS post Giardia
Clinical presentation with Giardia
Acute/chronic diarrhoea
flatulence
vomiting
Bali belly
OR asymptomatic
Diagnosis of Giardia
Faecal smear -> look for cysts
In acute stage may see trophozoite with 2 nuclei and a central spine
- Zinc sulphate floatation of cysts
- Giardia SNAP (cysts shedding is intermittent so may need to take a few samples over time)
- ELISA
- PCR
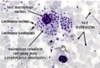
What is this?

Giardia cyst
Treatment of Giardia
Supportive care
Metronidazole (resistance) needs multiple doses for 5-7 days (can cause encephalopathy)
- Febantel for 3 days
- Fenbendazole for 5 days
Control of Giradia
Hygiene, reduce overcrowding and stress
- wash diarrhoea with ammonia
- wash bedding in hot soapy water - dry in sunlight
Trichomonads features
Faecal-oral transmission (fresh faeces)
Can be transmitted during sex
No cysts! Trophozoites only
Single nucleus
3-6 anterior fagella with one that forms undulating membrane
Bovine - Tritrichomonas foetus significance
Transmission?
Epidemiology?
Infertility and reduced pregnancy
- sexually transmitted through preseminal fluid (no transmission by AI)
- Bulls are asymptomatic carriers - survives in folds of penis
- extensive cattle farms (North QLD) with uncontrolled mating
Tritrichomonas blagurni infects what species?
Feline
Significance of Tritrichonomas blagburni
- Large bowl disease with chronic diarrhoea
- outbreaks in catteries
- asymptomatic carriers with chronnic shedding
Diagnosis of felin tritrichonomas
Fresh faecal smear and look for motile trophozoite
Faecal culture - grow trophozoites in anaerobic bag
PCR
Treatment of feline tritrichomoniasis
- off label use of ronidazole (30mg/kg) once daily for 14 days
- borad spectrum antibiotic -> use probiotic after treatment
- beware of neurotoxicity
Bovine tritrichomonas replication?
Uterine mucosa and causes infertility by disrupting the uterine membrane