Taeniid Cestodes Flashcards
(52 cards)
Significance of taeniids
livestock and meat industry
some zoonotic
clinical disease (humans)
Public health impact
What is a cysticercosis
Cyst in the IH
Random taenia facts
- Branched uterus
- unpaired genitals
- genital pores in irregular sequence on either side
Types of larval cysts
Cysticercus-> cysticercosis - Taenia
Coenurus-> coenuriasis - other Taenia
Hydatid-> hydatidosis - Echinococcus spp
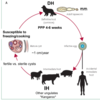
Taenia solium (pork measles worm) lifecycle and host
Egg -> Oncosphere -> Cysticercus (pig, humans, muscles/CNS) -> adult (humans)
Features of Taenia solium
- usually only 1 adult in SI (ie. solium)
- 5-10m long
Laval stage of Taenia solium
Affinity
Cysticercus cellulosae
Oncosphere carried in blood stream to brain, muscles and subcutis tissue. Affinity for nervous tissue
Taenia saginata IH
and DH
Cattle; musculature
Humans
Taenia saginata common name
size
larval stage name and distribution
beef measles worm
5-15m
Cysticercus bovis in muscles.
Lifecycles of human Taenia

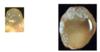
Which Taenia?
Taenia saginata
Which Taenia?

Teania solium
IH of Taenia ovis
Sheep, goat; musculature
DH of Taenia ovis
canid; dog and fox
Features of Cysticercus ovis
mostly in heart, diaphragm and masseter muscles
Cysts rapidly degenerate to form granulomas
What has caused these lesions?

Taenia hydatigena
IH of Taenia hydatigena
Ungulates; liver+omentum
DH of Taenia hydatigena
canid
Common name of Taenia hydatigena
False hydatid worm
Cysticercus tenuicollis (from T. hydatigena) features
attached to omentum in sheep, cattle, pigs.
oncosphers burrow through liver for 1 month -> peritoneal cavity and establishes in omentum
may lead to Black Disease
- liver condemnation
Taenia pisiformis IH
Rabbit, hares; liver+omentum
DH of T. pisiformis
canid
Cysticercus forming Taenia
T. solium
T. saginata
T. ovis
T. hydatigena
T. pisiformis
T. taeniaeformis
DH of T. taeniaeformis
Felid