quality assurance and fault analysis Flashcards
(76 cards)
purpose of quality assurance
The purpose of quality assurance (QA) in dental radiology is to ensure consistently adequate diagnostic information, whilst radiation doses to patients (and other persons) are kept ALARP, taking into account the relevant requirements of IRMER17 and IRR17”
- Faculty of general dental practitioners
- Go to guide for dentists for taking and using radiographs in practice
radiographs are good and safe
ALARP
as low as reasonably practicable
quality assurance programme
- Necessary in every dental practice/hospital
- Should cover all aspects of using radiographs
- Procedures (e.g. risk assessments, local rules, contingency plans, etc.)
- Staff training
- X-ray equipment
- Patient dose
- Image processing
- Display equipment
- Image quality
*
quality assurance programme created with
Created with input from a Medical Physics Expert (role defined in IRMER17)
- Should be at least one in every healthboard
quality assurance programme shoudl cover
all aspects of taking and using radiographs
- Procedures (e.g. risk assessments, local rules, contingency plans, etc.)
- Staff training
- X-ray equipment
- Patient dose
- Image processing
- Display equipment
- Image quality
- Who can take?*
- Where can take?*
- What to do if something goes* wrong?
QA of digital image receptors
frequency
- Digital receptors reusable, therefore wear & tear (& mishandling) will eventually impact image quality & necessitate replacement
- Should be formally checked on a regular basis
- e.g. every 3 months (or sooner if issue is suspected)
3 things to check on digital image receptor
Things to check
- The receptor itself
- Image uniformity
- Image quality
digital image receptor check
- Check for visible damage to casing/wiring e.g. scratches, bent, creases
- Check if clean (e.g. no congealed disinfectant/saliva)
image uniformity checks on digital image receptors
- Expose receptor to an unattenuated X-ray beam & check if resulting image is uniform
- i.e. should show a consistent shade of grey across the whole image no attenuation
image quality check on digital image receptor
Take a radiograph of a test object & assess the resulting image against a baseline (ideal image
damage on phosphor plates
Scratches - white lines (red)
Cracking (from flexing/bending) - network of white lines (yellow)
Delamination - white areas around edge (green)
- i.e. separation of phosphor layer from base plate – mishandling, wet and drying out

damage on solid state sensors
sensitive parts are encased so unlikely to get scratches
Sensor damage -> white squares/straight lines (dead pixels) Blue

damage on film receptors
Damage often appears as black marks due to sensitisation of radiographic emulsion
- Silver halide crystals are sensitised by something other than X-ray photons (heat, pressure) -> black marks
However, may appear white if emulsion is scraped off completely
Marks may represent nail marks, bite marks, fingerprints, etc.

scratches on phosphor plates
white lines

cracking from flexing or bending of phosphor plates ->
network of white lines

delamination on phosphor plates
white areas around edge of image
i.e. separation of phosphor layer from base plate – mishandling, wet and drying out

sensor damage to solid state sensors ->
white squares/straight lines (dead pixels)
sensitive parts are encased so unlikely to get scratches

sensitisation of film receptor damage
black marks
- Silver halide crystals are sensitised by something other than X-ray photons (heat, pressure)

white marks on film receptors
if damage causes emulsion to be completely scraped off

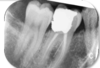
what caused this

Digital (phosphor plate)
- Crescent shaped well defined white mark superimposing the tooth
- Not normal radiographic anatomy
Nail mark

what caused this

Film
- Crescent shaped well defined black mark superimposing the root
Nail mark

what receptor damage is on these images (2 types)

Scraped causing scratches (orange)
Delamination (blue)
- Phosphor layer peel away from edge of image
- Mishandling, wet and drying
- Frayed appearance
Same receptor used twice – bad as obvious damage

white line on phosphor plate (digital receptor)

scratch

cracking on phosphor plate (digital receptor) seen as

network of white lines
due to flexing/bending