quiz 4 Flashcards
(31 cards)
1 Which is not transported by blood?
a. carbon dioxide b. hormones c. nutrients d. oxygen e. urine
e. urine
- How is blood protective?
a. The red blood cells perform phagocytosis.
b. Blood regulates endocrine glands.
c. Plasma cells produce antibodies.
d. Blood regulates pH of bodily fluids.
e. T-helper cells produce antibodies.
c. plasma cells produce antibodies
- Which pairing is mismatched?
a. cytotoxic T cells: attack viruses and cancer cells
b. neutrophils: secrete antibodies
c. eosinophils: involved in allergic reactions and digesting parasitic worms
d. basophils: involved in allergic reactions
e. T helper cells: secrete cytokines
b. neutrophils: secrete antibodies
- Which layer of the heart and its associated location/function is mismatched?
a. Endocardium: lines the inside of the heart
b. Myocardium: responsible for contraction of the heart
c. Epicardium: the visceral portion of the serous pericardium
d. Serous pericardium: tough connective tissue that anchors the heart
D. serious pericardium: tough connective tissue that anchors the heart
- The heart chamber with the thickest walls that pumps blood through the systemic circulation is t
a. Left atrium. b. Right atrium. c. Right ventricle. d. Left ventricle.
d. left ventricle
- The P wave of an ECG is created by the electrical activity associated with
a. Atrial depolarization.
b. Atrial repolarization.
c. Ventricular depolarization.
d. Ventricular repolarization.
e. Interventricular septum depolarization.
a. atrial depolarization
- At a normal resting heart rate, each cardiac cycle lasts approximately
a. 0.1 seconds.
b. 0.2 seconds.
c. 0.4 seconds.
d. 0.8 seconds.
e. 2.0 seconds.
d. 0.8 secs
T/F
- The beginning of an atherosclerotic plaque occurs when a “fatty streak” in the vessel wall is formed from macrophages eating accumulated LDL particles
true
T/F
- Neutrophils are agranular lymphocytes that phagocytize bacteria.
false
- Neutrophils are granular lymphocytes that phagocytize bacteria.
t/f
- Antibiotics are often used for treatment of pericarditis.
false
NSAIDs are often used for treatment of pericarditis
t/f
- When a blood vessel is damaged, platelets adhere to exposed keratin fibers and cause the fibers to produce a fibrin mesh called a clot.
false
When a blood vessel is damaged, platelets adhere to exposed collagen fibers and cause the platelets to produce a fibrin mesh called a clot
t/f
- Macrophages are WBCs that give rise to thrombocytes.
false
Megakaryocytes are WBCs that give rise to
- Exlplain why the some of the formed elements of the blood are considered incomplete. Also list which mature formed elemets are complete and which ones are incomplete (3 points)
WBC are complete
incomplete-lack a nucleus, thrombocytes and RBCs are incomplete
figure 1
figure 2
- Each of these pictures represent an erythrocyte at maturity. One represents erythrocytes with normal levels of oxygen; the other shows what happens during a specific disease of the blood when oxygen levels are low.
A) Specifically label each type of cell condition interms of “with sufficient oxygen” an “with low levels of oxygen”. B) Give one reason why the cell in Figure 2 looks the way it does. (2 points)
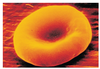
figure 1: with sufficient oxygen
figure 2: with low levels
the cell becomes sickle shaped because the Hb-S molecule collapses when oxygen levels are low and causes the RBC to shrink
Basophil
j. WBC that is involved in allergies
cytotoxic T cell
f. WBC that targets cancer cells and virus-infected cells
chylomicron
e. particle that transports dietary lipids through lymph and blood
dendritic cell
b. branched, phagocytic WBC found throughout the body, especially in the skin
eosinophil
i. WBC that is involved in allergies and digests parasitic worms
lymphatic tissue
c. composed of cells responsible for immunity and absorption of lipids
monocyte
a. becomes specialized in phagocytosis of cell debris and microbes during inflammation
neutrophil
g. WBC that is considered a bacterial “slayer”; most abundant WBC type
t cell
h. Lymphocyte that matures in the thymus; differentiates into specialized types
WBC
d. general term that includes all leukocytes


