quiz 4 Flashcards
(43 cards)
Covalent bonding of Ethers
C-O-C
straight chained or branched nonaromatic hydrocarbon?
Aliphatic hydrocarbons
Why is molecular length important?
anesthetic effect of immobility is decreased or lost if carbon atom chain length exceeds a distance of four or five carbon atoms 5 angstroms

Halothane
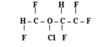
Isoflurane

desflurane

Sevoflurane
The addition of fluorine [F], chlorine [Cl], bromine [Br], or iodine [I] (Halogens) influences what anesthetic’s characteristics?
Potency - increases with heavier halogens AMU (Bromine)
Arrhythmogenic properties - more halogens, more arrythmias
Chemical stability - Enhance
Flammability - Reduced
What halogens are Disinfectants?
Bromine
Iodine
Chlorine
Typically , increasing the number of _______ atoms on an anesthetic molecule slows biodegradation.
fluorine
Currently used Volatile gas with most percentage liver metabolism?
Sevoflurane (5%)
(Halothane was 45%)
Absorption phase term?
Uptake
Metabolic phase term?
Biotransformation
Excretion phase term?
Elimination
Myer Overton Rule?
Lipid solubility is directly proportional to potency
A reduction in body temperature ______ anesthetic requirement
lowers
mediate ________ via glycine, sodium and NMDA receptors
Supraspinal Effects, causes amnesia
weak inward-rectifying K+ Channels, and inhibiting glycine and GABA receptors
Spinal Effects causing immobility
MAC % of Halothane
0.75%
Inhaled anesthetics “PROBABLY” produce anesthesia by ?
enhancing the function of inhibitory ion channels and by blocking the function of excitatory ion channels
Inhibitory channels?
Glycine
GABA
Effects of hypnosis are from what receptor?
GABA
Hyperpolarization of GABA when?
Influx of Cl- ions


