RAT 4 Flashcards
(73 cards)
inferior olivary nucleus
compares the motor plan with the sensory information coming in
sends summated information output to the cerebellum as “climbing fibers”
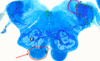
Identify 3

middle cerebellar peduncle; gets input from the pontine nuclei to project to the lateral hemisphere of the cerebellar cortex (cerebrocerebellar circuit = motor planning and learning)
Identify 1

superior cerebellar peduncle in the wall of the fourth ventricle
output of the cerebrocerebellar tract; from dentate nucleus to red nucleus and VL of thalamus
Identify 2

main sensory and motor of V at the elvel of the upper pons
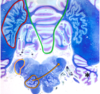
Identify pink outline

reticular formation which give rise to the medial reticulospinals
note that the red outline is the general locaiton of the corticospinal and corticoreticulars
what is outlined in red?
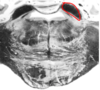
superior cerebellar peduncle; site at which axons leave SCP and decussate to contralateral side (Where they go to red nucleus and VL of thalamus)
where are corticopontine fibers located
crus cerebri
(in yellow outline)

Through which cerebellar peduncle do the dentatorubrothalamic axons pass?
these are the axons coming from the superior cerebellar peduncle to go to the red nucleus and ventrolateral thalamus
identify what is circled in yellow

subthalamic nuc
lesion to cerebellar vermis
truncal ataxia (wide-based, drunken sailor gait)
dysarthria
lesion to cerebellar hemisphere
intention tremor
limb ataxia
loss of balance
ipsilateral!! FALL TOWARD LESION
PPRF lesion
eyes look away from lesion
lesion to the mamillary bodies
Wernike Korsakoff syndrome
Confusion, Ataxia, Nystagmus, Opthalmoplegia
memory loss, personality changes
what coudl cause lesion to amygdala
HSV1 encephalitis
what would an amygdala lesion cause
disinhibited behavior
lesion at red nucleus
decrebrate posturing
reseting tremor
parkinsons ; uncontrolled mvmt of distal apendages ; alleviated by intentional movement
intention tremor
cerebellar dysfunciton
slow, zigzag motion when pointing/extending toward a target
what spinal tract is involved with the control of trunk muscles?
anterior corticospinal
another name for the anterolateral system
anterior spinothalamic tract
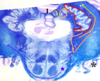
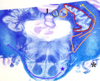
Identify 1

caudate
Identify 2
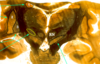
putamen
Idenitfy 3

globus pallidus
striatum
caudate and putamen