Final but non rat Flashcards
(205 cards)
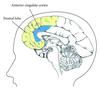
main goal of limbic system
conscious awareness of autonomic function
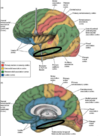
anterior hypothalamus
paraventricular nucleus suprachiasmatic nucleus prep-tic nucleus ventrolateral prep-tic area (VLPO)
paraventricular nucleus
magnocellular (oxytocin and ADH) parvocellular (ACTH, TSH, descending autonomics) anterior hypothalamus
preoptic nucleus
temp regulation anterior hypothalamus
suprachismatic nucleus
circadian rhythm anterior hypothalamus
ventrolateral preoptic area
sleep via inhibition of arousal anterior hypothalamus
Middle hypothalamus
arcuate nucleus ventromedial nucleus
NPY/AgPR
stimulates appetite
CART/alphaMSH
inhibits feeding
arcuate nucleus
stimulates (MPY/AgRP) or inhibits (CART/alphaMSH) feeding middle hypothalamus
ventromedial nuclei
appetite, weight gain, insulin regulation
posterior hypothalamus
mammillary nuclei orexin/hypocretin and histamine neurons
orexin/hypocretin and histamine neurons
arousal posterior hypothalamus
mammillary nuclei
emotion and short term memory posterior hypothalamus
neurons that are a part of the arousal network
- NT release and neuronal activity HIGHEST during WAKE and lowest during sleep
- Treatment with agonists promote physiological and behavioral indicators of wakefulness
- Treatment with antagonists (or lesions, disease) promote physiological and behavioral indicators of sleep
I neurons
inspiration neurons
stimulate neurons that innervate resp muscles
E neurons
expiration neurons
inhibit I neurons
ghrelin
hunger hormone; released when stomach empty
CCK
released from duodenum and upper intestine when aa and FA in GI tract; signals satiety
short term regulators of hunger
Ghrelin and CCK
long term regulator of hunger
leptin
what senses hypertonicity of the blood?
vascular organ of the lamina terminalis (OVLT)
when it detects an incr in blood solutes –> stimulates ADH release (antrior hypothalamus) and produces thirst (via lateral hypothalamus)
what detects hypovolemia?
kidneys and mechanoreceptors in blood vessel walls –> if hypovolemia is detected, trigger thirst and drinking in lateral hypothalamus and ADH releas (via paraventricular nucleus in the anterior hypothalamus)
signs of cerebellar dysfunciton
DANISH
dysdiadochokinesia and dysmetria
ataxia
nystagmus
intention tremor
slurred speech
hypotonia