Rhoton's I Flashcards
(500 cards)
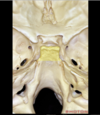
1
Q

A
Atlas
2
Q

A
Axis
3
Q

A
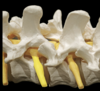
Uncinate process
The uncinate process of the cervical spine is a hook-shaped process found bilaterally on the superolateral margin of the cervical vertebral bodies of C3-C7.
The uncinate processes are more anteriorly positioned in the upper cervical spine and more posteriorly location in the lower cervical spine.

4
Q

A
Odontoid process
5
Q

A
Superior articular facet for joint with occipital condyle
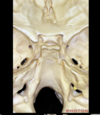
6
Q
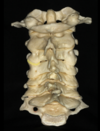
A
Facet joint

7
Q
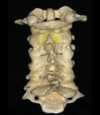
A
Lamina
8
Q

A
Lateral mass
9
Q

A
Spinous process
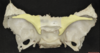
10
Q

A
Transverse foramen
11
Q

A
V2
12
Q

A
V3
13
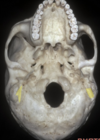
Q

A
Facet joint
14
Q

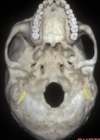
A
Lamina
15
Q

A
Odontoid process
16
Q
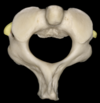
A
Transverse process
17
Q

A
Facet joint
18
Q
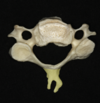
A
Spinous process
19
Q

A
Pedicle
20
Q

A
Superior articular process
21
Q

A
Lateral mass
22
Q
A
Nerve roots
23
Q

A
Facet joints
24
Q

A
Arcuate eminence
25

Carotid groove of sphenoid bone
26

Meatal depression
27

Petrous temporal bone
28

Sigmoid sinus
29
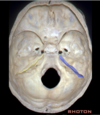
Superior petrosal sinus
30

Tegmen
31

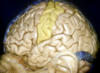
Torcula
32

Trigeminal prominence
33

Tuberculum sella
34
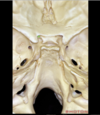
Relations of the sphenoid bone

Frontal and ethmoid anteriorly
Squamosal temporal bone laterally
Posteriorly the petrous temporal and occipital bone
35
What bones form the foramen lacerum?
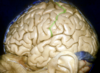
Foramen lacerum formed by the junction of the petrous apex, sphenoid bone and occipital bone

36
What bounds the lateral edge of the carotid groove of the sphenoid bone?

The lingula

37
Optic canal
38
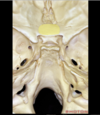
Planum sphenoidale which forms the roof of the sphenoid sinus
39

Dorsum sella which forms the upper clivus
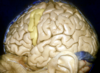
40
What structure runs here?

This is the petroclival fissure in which the inferior petrosal sinus runs
41
Intrajugular portion of the temporal bone
42

Anterior clinoid process
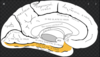
43

Anterior limbus of chiasmatic sulcus
44

Body of the sphenoid bone
45

Chiasmatic sulcus
46

Dorsum sella
47

Greater wing of sphenoid
48
Lesser wing of sphenoid
49

Posterior clinoid process
50

Sella turcica
51

Tuberculum sella
52

Vidian canal
53

Carotid canal
54

Infratemporal crest
55

Infratemporal fossa
56
Mastoid notch
57

Maxillary sinus
58
Occipital groove
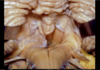
59

Pterygoid process
60

Petroclival fissure
61

Foramen rotundum
62

Median pterygoid plate
63

Vidian canal
64
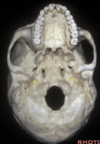
Carotid canal
65
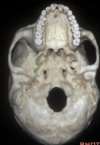
Foramen ovale
66

Foramen spinosum
67
Etymology- sella turcica
Turkish saddle
68
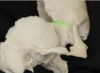
Pterion
69

Sphenosquamosal suture
70

Temporal fossa
71

Zygoma
72

Zygomatic arch
73

Anterior clinoid process
74

Anterior ethmoid canal
75

Body of sphenoid
76

Ethmoidomaxillary suture
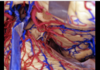
77

Frontal process of maxilla
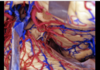
78

Frontoethmoidal suture
79

Greater wing of sphenoid
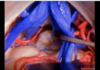
80
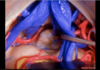
Inferior orbital fissure
81

Infraorbital canal
82
Infraorbital foramen
83
Contents of the infraorbital canal
Infraorbital nerve (V2)
Infraorbital artery (Maxillary artery)

84
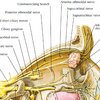
Contents of the anterior ethmoidal foramen
Anterior ethmoidal artery and vein
Anterior ethmoidal nerve, branch of nasociliary (V1)
85

Lacrimal bone
86

Lesser wing of sphenoid
87

Maxilla
88

Optic canal
89
Contents of optic canal
Opthalmic artery
Optic nerve
90
Contents of the inferior orbital fissure
Inferior Orbit Gets Infra-Orbital Nerves And VeinZ
IO: inferior ophthalmic vein (a tributary to both pterygoid venous plexus and cavernous sinus)
G: ganglionic branches from the pterygopalatine ganglion to maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve
ION: infra-orbital nerve (branch CN V2)
A: infra-orbital artery (branch maxillary artery)
V: infra-orbital vein (drains inferior orbit, communicates with the inferior ophthalmic vein, a tributary to pterygoid venous plexus)
Z: zygomatic nerve (branch CN V2)

91

Optic strut
92

Orbital plate of ethmoid bone
93

Orbital process of palatine bone
94

Posterior ethmoid foramen
95
Contents of the posterior ethmoid foramen
Posterior ethmoidal foramen opens at the back part of this margin under cover of the projecting lamina of the sphenoid, and transmits the posterior ethmoidal vessels and nerve.

96

Sphenoethmoidal suture
97

SOF
98
Contents of SOF
Long Fissures Seem To Store Only Nerves, Instead Of Arteries, Including Ophthalmic Veins (Superior to Inferior)
L: lacrimal nerve (branch of CN V1)
F: frontal nerve (branch of CN V1)
S: superior ophthalmic vein (a tributary to cavernous sinus)
T: trochlear nerve (CN IV)
SO: superior division of the oculomotor nerve (CN III)
N: nasociliary nerve (branch of CN V1)
IO: inferior division of the oculomotor nerve (CN III)
A: abducens nerve (CN VI)
IOV: inferior ophthalmic vein (tributary to both cavernous sinus and pterygoid venous plexus)

99

Hiatus of the endolymphatic sac
100

Hook of the sigmoid sinus
101
Inferior petrosal sinus (which runs in the petroclival fissure)
102
Jugular foramen
103
Contents of the jugular foramen
Pars nervosa:
Inferior petrosal sinus
IX + Jacobson's (tympanic canaliculus)
Pars vasculosa:
IJV
X, XI
Nerve of Arnold (mastoid canaliculus)
Posterior meningeal artery

104
Porus of the IAM
105

Cochlear area of IAM
106

Facial canal
107

Inferior vestibular area
108

Singular foramen
It carries the singular nerve, which is also known as the posterior ampullary nerve and is a branch of the inferior vestibular nerve that carries afferent information from the posterior semicircular canal
109

Superior vestibular area
110

Transverse (falciform) crest
111

Vertical crest
Bill's bar
112
Contents of singular foramen
The foramen singulare, also known as the singular foramen, is a small opening at the posteroinferior aspect of the fundus of the internal auditory canal (IAC)
It carries the singular or posterior ampullary nerve, a branch of the inferior vestibular nerve which carries afferent information from the posterior semicircular canal
113

Central sulcus
114
Frontal lobe
115

Inferior frontal gyrus
116

Middle frontal gyrus
117
Occipital lobe
118

Parietal lobe
119

Parieto-occipital sulcus
120

Pre-occipital notch
121

Supramarginal gyrus
122

Sylvian fissure
123

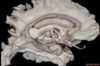
Temporal lobe
124
Central lobe
125

Central sulcus
126

Frontal lobe
127

Inferior frontal gyrus
128

Inferior frontal sulcus
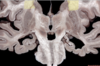
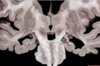
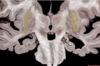
129

Middle frontal gyrus
130

Middle temporal gyrus
131

Occipital lobe
132

Parietal lobe
133

Post central gyrus
134
Postcentral sulcus
135

Precentral gyrus
136

Precentral sulcus
137
Premotor cortex
138

Subcentral gyrus
139

Superior frontal gyrus
140

Supramarginal gyrus
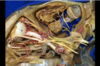
141

Vein of Trolard
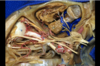
142

Ambient cistern
143

Anterior medial temporal lobe
144

Calcarine sulcus
145

Central lobe
146

Cingulate gyrus
147

Cingulate sulcus
148

Corpus callosum
149

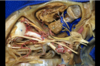
Cuneus
150

Fusiform gyrus
151

Lingual gyrus
152

Marginal ramus of the cingulate sulcus
153

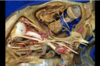
Middle media temporal lobe
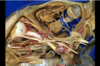
154

Paracentral lobule
155

Paracentral sulcus
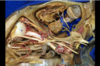
156
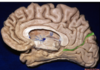
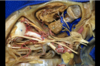
Parieto-occipital sulcus
157

Precuneus
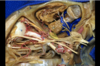
158

Quadrigeminal cistern
159
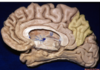
Superior parietal lobule
160

Supplementary motor area
161
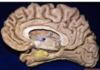
Uncus
162

Cerebellar tonsils
163

Cerebellar vermis
164
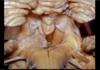
Cerebral aqueduct
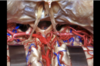
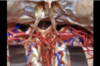
165

Floor of the 4th ventricle
166

Inferior medullary velum
167

Superior lateral recess of the fourth
168

Tonsil of cerebellum
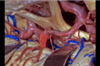
169
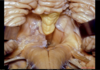
Uvula of vermis
170
Floculus
171

Superior cerebellar peduncle
172

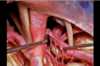
Inferior medullary velum
173

Tela choroidea

174

Abducens
175

Auditory nerve
176

Cerebral peduncle
177

Choroid plexus
178

Facial nerve
179

Foramen of Luschka
180

Glossopharyngeal nerve
181

Rootlets of hypoglossal nerve
182

Lateral margin of the pons
183

Pontomedullary sulcus
184

Spinal portion of accessory
185

Trigeminal
186

Vagus
187

Flocculus
188
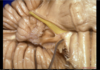
Auditory nerve
189

Cerebellopontine angle
190

Facial nerve
191

Foramen of Luschka
192

Glossopharyngeal nerve
193

Abducens nerve
194

AICA
195

Auditory nerve
196
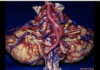
Axilla of the trigeminal nerve
197

Oculomotor nerve
198

PICA
199
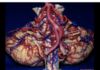
SCA
200

Ambient cistern
201

Bridging veins
202

Pineal gland
203
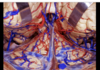
Posterior cerebral artery
204

Quadrigeminal cistern
205
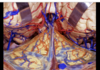
Tentorium
206

Ambient cistern
207

Collicular plate
208

Internal cerebral veins
209

Pineal gland
210

Posterior cerebral artery
211
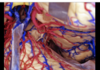
Splenium of the corpus callosum
212
Straight sinus
213

Trochlear nerve
214
Vein of Galen
215

Inferior colliculi
216

Pineal gland
217

Superior colliculus
218
Basal vein of Rosenthal

219
Inferior colliculus
220

Internal cerebral vein
221

Medial posterior choroidal artery
Branch of P2
222

Pineal gland
223

Superior colliculus
224

Tentorium
225

Velum interpositum

226
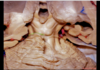
Cerebellomesencephalic fissure
227

Anterior commissure
228

Body of fornix
229

Body of the lateral ventricle
230

Choroid plexus
231

Column of fornix
232

ISS
233

Internal cerebral vein
234

Lamina terminalis
235

Mamillary body
236

Optic chiasm
237

Pineal gland
238

Pituitary stalk
239
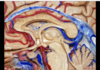
Precentral vein
240

Straight sinus
241

Vein of Galen
242

Velum interpositum
243

Area postrema
244
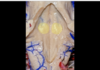
Facial colliculi
245

Hypoglossal trigone
246

Median sulcus
247
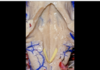
Vagal triangle
248

Lateral ventricles
249

Choroid plexus
250

Corpus callosum
251

Genu of internal capsule
252

Thalamostriate vein
Note choroid plexus is medial to thalamostriate
253
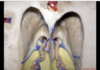
Thalamus
254

Fornix
255

Internal cerebral vein
256

Septal vein
257

Superior choroidal vein
258

Velum interpositum
259

Thalamostriate vein
260

Velum interpositum
261

Internal cerebral vein
262

Medial posterior choroidal artery
263

Tela choroidea
264
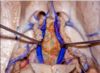
Velum interpositum
265

Ambient cistern
266

Anterior commissure
267

Choroidal fissure
268

Columns of fornix
269

Foramen of Monro
270

Infundibular recess of the third ventricle
271

Lamina terminalis
272

Lateral geniculate body
273

Massa intermedia
274

Oculomotor nerve
275

Posterior commissure
276

Quadrigeminal cistern
277

Velum interpositum
278

Atrium of the lateral ventricle
279

Calcar avis
The calcar avis, previously known as the hippocampus minor,[1] is an involution of the wall of the lateral ventricle's posterior cornu produced by the calcarine fissure
280

Crural cistern
281

Ambient cistern
282
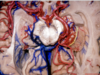
Fimbria of fornix
283

Lateral posterior choroidal artery
Branch of P2
284
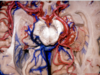
Medial posterior choroidal artery
285
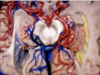
Optic radiations
286

P1
287

P2
288
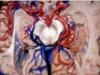
PComm
289

Pulvinar
290

Ambient cistern
291

Body of fornix
292
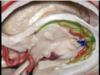
Choroidal fissure
293

Crus of fornix
294

Fimbria of fornix
295
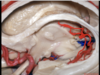
Medial posterior choroidal artery
296

Pineal gland
297

PCA
298

Stria medullaris thalami
299

Velum interpositum
superiorly: the columns of the fornices and hippocampal commissure (psalterium) reaching as far forward as the foramen of Monro
inferiorly: the internal cerebral veins and tela choroidea of the third ventricle
inferolaterally: the thalamus
posteriorly: the narrow base of the triangle abuts the splenium of the corpus callosum
300

Internal cerebral vein
301

Septal vein
302

Superior choroidal vein
303

Thalamostriate vein
304

Angular gyrus
305

Inferior longitudinal fasciculus
306
Middle longitudinal fasciculus
307

Superior longitudinal fasciculus II
308

Short association fibres
309
Arcuate fasciculus
310

Broca's area
311
Extreme capsule
312

Inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus
313
Function IFOF
The inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus (IFOF) is a large white matter tract of the human cerebrum with functional connectivity associated with semantic language processing and goal-oriented behavior.
314
Function SLF II
SLF II is the major component of SLF and originates in the caudal-inferior parietal cortex and terminates in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (Brodmann 6, 8 and 46).
SLF II connects to the caudal inferior parietal cortex which controls spatial attention and visual and oculomotor functions. This suggests the SLF II provides the prefrontal cortex with parietal cortex information regarding perception of visual space. Since these bundles are bi-directional, working memory (Brodmann 46) in the prefrontal cortex may provide the parietal cortex with information to focus spatial attention and regulate selection and retrieval of spatial information.
315
Function MLF
The medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) is a myelinated composite fibre tract found in the brainstem. The MLF primarily serves to coordinate the conjugate movement of the eyes and associated head and neck movements.
316

ILF
317
Function ILF
The inferior longitudinal fasciculus carries visual information from occipital areas to the temporal lobe (Catani et al., 2003a) and it is likely to play an important role in visual object recognition, semantic processing and in linking object representations to their lexical labels

318

Uncinate fasciculus
319
Function uncinate fasciculus
Function. The function of the uncinate fasciculus is not known, though it is traditionally considered to be part of the limbic system.. It has been proposed that the uncinate fasciculus allows mnemonic representations stored in the temporal lobe to interact with and guide decision making in the frontal lobe

320

Wernicke's area
321

Claustrum
322

IFOF
323

Putamen
324

Ventral external capsule
325

Atrium of the lateral ventricle
326

Lateral geniculate body
327

Meyer's loop

328

Optic radiations
329

Tapetum of the corpus callosum
330

Temporal horn of the lateral ventricle
331

Lateral geniculate body
332

Meyer's loop
333

Cingulum
334

Corpus callosum
335
Etymology- carotid
from the greek "karotis"
early 17th century: from French carotide or modern Latin carotides, from Greek karōtides, plural of karōtis ‘drowsiness’, from karoun ‘stupefy’ (because compression of these arteries was thought to cause stupor).
336
Etymology- sphenoid
mid 18th century: from modern Latin sphenoides, from Greek sphēnoeidēs, from sphēn ‘wedge’.
337
Contents of vidian canal
Nerve of pterygoid canal, (Vidian nerve),
the artery of the pterygoid canal (Vidian artery),
and the vein of the pterygoid canal (Vidian vein)
338
Nerve of pterygoid canal
Formed by the union of the greater petrosal nerve (CN VII PNS) and the deep petrosal nerve (SNS)
PNS fibres synapse in the pterygopalatine ganglion

339
Vidian artery
Branch of maxillary (ECA) and petrous part of ICA.
Can serve as an anastomosis between ICA and ECA
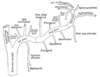
340

Amygdala
341
Anterior commissure
342

Cingulum
343

Corpus callosum
344

Fornix
345

Hippocampus
346

Internal capsule
347

Mamillary body
348

Mammillothalamic fasciculus
349

Nucleus accumbens
350

Velum interpositum
351

Caudate nucleus
352

Claustrum
353
Corona radiata
354
External capsule
355

Extreme capsule
356

Globus pallidus
357

Insula
358

Internal capsule
359

Frontoparietal operculum
360
Putamen
361

Substantia nigra
362

Subthalamic nucleus
363
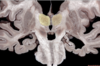
Thalamus
364

ACA
365

Crista Galli
366

Olfactory bulb
367
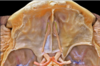
Olfactory groove
368
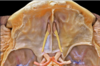
Olfactory tract
369

Optic nerve
370

Orbital roof
371

Planum sphenoidale
372

Abducens
373
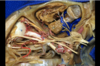
Anterior ethmoidal arteries
374

Anterior ethmoidal nerve
375

Anterior fossa
376
Cavernous sinus
377
Clinoidal segment of ICA
378

Ethmoid sinus
379

Facial nerve
380

Frontal nerve
381

Frontal sinus
382

Geniculate ganglion
383

Greater petrosal nerve
384

Infratemporal fossa
385

Infratrochlear nerve
386

Lacrimal gland
387

Lacrimal nerve
388

Lateral rectus
389

Lateral wall of orbit
390

Long ciliary nerves
391

Mandibular nerve
392
Maxillary nerve
393

Meatal segment of facial nerve
394

Middle fossa
395

Nasociliary nerve
396

Oculomotor nerve
397

Olfactory bulb
398

Ophthalmic artery
399

Ophthalmic nerve
400
Ophthalmic segment of ICA
401

Optic canal
402
Optic nerve
403

Optic nerve sheath
404

Orbit
405

Orbital apex
406
Petrosphenoidal ligament
407
Pituitary gland
408

Pituitary stalk
409

Posterior ethmoidal artery
410
Pterygopalatine fossa
411

Sphenoid sinus
412

Superior hypophyseal artery
413
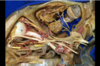
Superior oblique muscle of orbit
414

SOF
415

Superior vestibular nerve
416
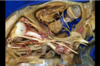
Supraorbital nerve

417
How does the supratrochlear nerve leave the orbit?
The supratrochlear nerve then exits the orbit between the pulley of the superior oblique and the supraorbital foramen, curves up on to the forehead close to the bone, and ascends beneath the corrugator supercilii and frontalis muscles.
418

Supratrochlear nerve
419

Temporal fossa
420

Trigeminal ganglion
421
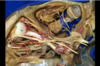
Motor root of trigeminal nerve
422
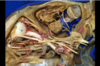
Trochlear nerve
423

A1
424
ACA
425

ICA
426
Lamina terminalis
427

MCA
428

Cerebral aqueduct
429

Third ventricle
430

A1 segment of ACA
431
A2 segment of ACA
432

ACA
433

AComm
434

ICA
435

MCA
436

ACA
437

Anterior choroidal artery
438
Communicating segment of ICA (C7)
439

MCA
440

Oculomotor nerve
441

Ophthalmic segment of ICA
442

Optic nerve
443

Perforating branches of PComm
444

PComm
445

SCA
446

Supraclinoid ICA (C6)
447

Abducens
448

Anterior clinoid process
449

Greater petrosal nerve
450

ICA
451

Maxillary nerve
452

Meckel's cave
453
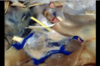
Oculomotor nerve
454

Optic nerve
455

SOF
456

Superior petrosal sinus
457

Tentorial edge
458
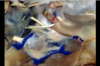
Trochlear nerve
459

Trigeminal nerve
460

Abducens nerve
461

Anterolateral triangle
462

Anteromedial triangle
463

Cavernous sinus
464

Clinoidal segment of ICA
465

Foramen ovale
466
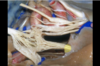
Foramen rotundum

467

Inferior division of oculomotor nerve
468

Mandibular branch of trigeminal
469

Maxillary nerve
470

Oculomotor nerve
471

Ophthalmic artery
472

Ophthalmic nerve
473

Optic nerve
474

Optic nerve sheath
475

Optic strut
476

Orbital apex
477

Sphenoid sinus
478

Superior division of oculomotor
479

SOF
480

Trochlear nerve
481

Vidian nerve
482

Anterolateral triangle
483

Anteromedial triangle
484

Arcuate eminence
485

Cavernous sinus
486

Clinoidal triangle
487

Cochlear
488

Foramen spinosum
489

Greater petrosal nerve
490

Inferior orbital fissure
491

Infratemporal fossa
492

Infratrochlear triangle (Parkinson's)
493

IAC
494

Lateral wall of orbit
495

Lesser petrosal nerve

496

Mandibular nerve
497

Middle meningeal artery
498

Oculomotor triangle
499

Optic canal
500

Orbit


