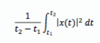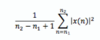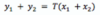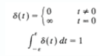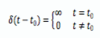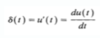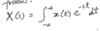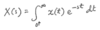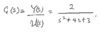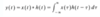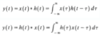Signals and Systems Flashcards
(161 cards)
What are samples?
Points of data
What are sampling intervals?
The distance between the sample points
Discrete-time signals can be defined in 2 ways…
- As a function
- As a list of values of a sequence
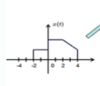
In this picture, the arrow indicates….?
And if the arrow is not shown, where is the ____ point?
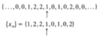
The n=0 point
The first value in the sequence is the n=0 point
Define analog signals
Analog Signals: An analog signal is a continuous-time signal x(t) that can take on any value in the continuous interval (a, b), where a may be - ∞ and b may be +∞.
Define Digital Signals
Digital Signals: A digital signal is a discrete-time signal x[n] that can only take on only a finite number of distinct values.
What is a real signal?
Real Signals: A signal x(t) is said to be a real signal if its value is a real
number
What is a complex signal?
Complex Signals: A signal x(t) is said to be a complex signal if its value is a complex number
A general (continuous- or discrete-time) complex signal x(t) is a function of the form
where x1(t) and x2(t) are real signals and j = √−1

Define Deterministic Signals
Deterministic Signals: Those signals whose values are exactly specified for any given time in the time span of interest are called deterministic signals. Such signals may be represented by a known function of time t.
Define Random Signals
Random Signals: Those signals that take random values at any given time are called random or non-deterministic signals. Such signals must be characterized statistically (that is, represented in probabilistic terms)
Any signal x(t) or x[n] can be expressed as a sum of ____ ____, one of which is ____ and one of which is ____
Any signal x(t) or x[n] can be expressed as a sum of two signals, one of which is even and one of which is odd
The product of two even signals or of two odd signals is a…?
…even signal
The product of an even signal and an odd signal is an…?
…odd signal
Define Periodic continuous-time signals
Periodic Continuous-time Signals: A continuous-time signal x(t) is said to be a periodic signal with period T if there is a unique positive nonzero value of T for which the following expression is valid
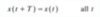
A dc signal is a signal in which x(t) is ____; such a signal is not periodic since its fundamental period is ____
A dc signal is a signal in which x(t) is constant; such a signal is not periodic since its fundamental period is undefined
Define Aperiodic Continuous-time Signals
Aperiodic Continuous-time Signals: Any continuous-time signal which is not periodic is called a non-periodic signal or an aperiodic signal
Define Periodic Discrete-time Signals
Periodic Discrete-time Signals: A sequence (discrete-time signal) x[n] is periodic with period N if there is a unique positive integer N for which the following expression is valid
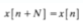
Define Aperiodic Discrete-time Signals
Aperiodic Discrete-time Signals: Any sequence which is not periodic is called a non-periodic sequence or an aperiodic sequence
A sequence obtained by uniform sampling of a periodic continuous-time signal may…
…not be periodic
The sum of two continuous-time periodic signals may…
… not be periodic
The sum of two periodic sequences is…
…always periodic
For any continuous-time signal x(t), the total energy of the signal over the interval t1 ≤ t ≤ t2 is defined as
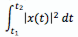
The average power of the signal x(t) over the interval t1 ≤ t ≤ t2 is defined as