Skeletal Muscle Flashcards
(13 cards)
What is the basic functional unit of skeletal muscle?
Sarcomere
Sarcomeres are made up of two kinds of protein filaments, thick and thin. Which protein makes up each filament?
- myosin (thick)
-
actin (thin)
- troponin
- tropomyosin
[Mnemonic]
“Act thin is thin.”
(how to remember which muscular filament is thin)
“Act thin is thin.”
Actin is the thin filament.
[Mnemonic]
Actin: Troponin and Tropomyosin
(how to remember which filament in a sarcomere is associated with troponin and tropomyosin)
Actin: Troponin and Tropomyosin
The thin filament of a sarcomere is made up of actin along with troponin and tropomyosin.
Which bands or zones of a sarcomere shorten during muscle contraction?
- H zone
- I band
[Mnemonic]
H zone and I band shortens like the waves in HI.
(how to remember which band or zone in a sarcomere shortens)
H zone and I band shortens like the waves in HI.
H zone and I bands shorten during contraction, similar to waves in Hawaii (HI).
Which bands or zones of a sarcomere does NOT change its length during muscle contraction?
A band
Because it’s the entire length of the myosin filament.
[Mnemonic]
A bands Always the same length.
(how to remember which band in a sarcomere stays the same length)
A bands are Always the same length.
What are the three main parts of a myocyte (muscle cell)?
- sarcolemma
- sarcoplasmic reticulum (specialized ER that contains many Ca2+ ions)
- T-tubules
Where in a muscle fiber are calcium (Ca2+) ions released from?
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
How does troponin and tropomyosin regulate muscle contraction?
Block the myosin-binding sites on actin, which prevents myosin heads from binding.
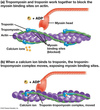
During muscle contraction, what happens when calcium ions bind to troponin?
Causes a conformational change in tropomyosin which exposes the myosin-binding sites.
Explain the sliding filament model of muscle contraction.
Myosin heads bind and release an actin filament. The two filaments slide past each other which shortens the sarcomere.


