Skillstorm Intro to Coding - OOP & Java Fundamentals Flashcards
(97 cards)
What are classes in Java?
They are blueprints used to define objects
What are a few examples of classes?
- Real-world objects
- Application components
What are the members of a Class in Java?
=> Variables (State)
=> Methods (Behavior)
=> Constructors (Initialization)
Given the following code, identify the class body, constructor, method body, and variable.
public class HelloVehicle {
int speed;
void accelerate() {}
HelloVehicle() {
speed = 0;
}
}
public class HelloVehicle { // class body
int speed; // variable
void accelerate() {} //method body
HelloVehicle() {
speed = 0;
} // constructor
}
Given a basic HelloWorld class, what’s the best way to write the signature of the main method in Java?
public class HelloWorld {
}
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(“Hello World”);
}
}
Which is the correct signature of the main method?
- public static void main(String[] args)
- static public void main(String[] args)
Both 1. and 2. are correct!!!
Label the separate code blocks correctly with following labels: Class, Constructor, Method, and Variable
- ____________
public class HelloVehicle{
2._____________
int speed;
3._____________
void accelerate() {}
4._____________
HelloVehicle(){
speed = 0;
}
}
- Class
public class HelloVehicle {
- Variable
int speed;
- Method
void accelerate() {}
- Constructor
HelloVehicle(){
speed = 0;
}
}
Java is strongly-typed, in other words, you have to state what data type each variable is going to be? True or False
True
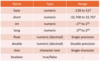
What are the four data types in Java and their sub-types?
- Numeric (whole)
- byte: -128 to 127
- short: -32,768 to 32,767
- int: -2^31 to 2^31
- long: -2^64 to 2^64
- Numeric (decimal)
- float: single precision
- double: double precision
- Text
- char: single character
- True/False
- boolean
What are non-primitive data types with an example?
Non-Primitive Data Types
- Any class you want
- Create your own types
For Example,
Vehicle Class as a variable to be used with an Engine Class
String
- Multiple characters together
You could string characters together to get a word such as HELLO.
In Java arrays, you store multiple values in a _____ _____ variable
single reference
Are Java arrays continuous?
Yes, they are a sequential block of memory
How do you access the elements of a Java array?
By their index
Though values can be different in each index of a Java array, can they also be of a different data type?
No. They have to be the same data type but can be different values
For Example:
If the data type is char, index 0 can have raj, index 1 can have hudek and so on, but index 3 could not have 42 because that is a numeric data type which is different than the original char data type we started out with in index 0 and index 1.
What do constructors initialize?
An object’s state
Calling a constructor by its new keyword does what?
It creates an object at runtime
Does Java provide a default constructor?
Yes, BUT only if you haven’t provided your own
Can you define many constructors and if so, what would that be called?
Yes, and it is known as constructor overloading
When a class contains a constructor, and you have more than one keyword, what happens when you call the second keyword?
The constructor is invoked to create a brand new object with its own state.
If you call the second reference variable (keyword) in a constructor, will the method from the class that acted on the first reference variable work here as well?
No
Why can’t you write two constructors that have the same number and type of arguments for the same class?
Because the compiler would not be able to tell them apart!
What happens if you don’t provide any constructors for your class?
The compiler automatically provides a no-argument, default constructor for any class without constructors.
How do you have variables that are common to all objects?
By using a static modifier
What does it mean that a static modifier is called a static field or class variable?
It means they are associated with the class, rather than any with any object.




