Spotter Qs Flashcards
(130 cards)
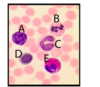
Which congenital heart defect can be identified in this image?
Patent foramen ovale
Atrial septal defect
Patent ductus arteriosus
Ventricular septal defect
Tetralogy of Fallot

Which congenital heart defect can be identified in this image?
Patent foramen ovale
Atrial septal defect
Patent ductus arteriosus
Ventricular septal defect
Tetralogy of Fallot
which muscles move the arm into this position? [2]

deltoid
supraspinatous
which cranial nerve is affected in this patient?

trigeminal
which segmental level is being assessed here?

S1
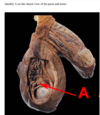
structure E is WHAT? [1]

white ramus
In this cross section of a peripheral nerve, what type of fibre has a morphology as illustrated by C?
- C axon
- A-beta axon
- A-gamma axon
- A-alpha axon
- A-delta axon

In this cross section of a peripheral nerve, what type of fibre has a morphology as illustrated by C?
- C axon
- A-beta axon
- A-gamma axon
- A-alpha axon
* *5. A-delta axon**

Which pathway runs through the region indicated by the asterisk?
- Lateral lemniscus
- Spinothalamic tract
- Vestibulospinal tract
- Corticospinal tractt
- Spinocerebellar tract

Which pathway runs through the region indicated by the asterisk?
- Lateral lemniscus
- Spinothalamic tract
- Vestibulospinal tract
* *4. Corticospinal tractt** - Spinocerebellar tract

In order to perform a lumbar puncture, the needle should inserted at position
A
B
C
D
E

In order to perform a lumbar puncture, the needle should inserted at position
A
B
C
D
E
Identify the structure indicated by the arrow that helps stablise the hip joint
- long head of biceps tendon
- articular capsule
- acetabular labrum
- acetabular ligament
- ligamentum teres

Identify the structure indicated by the arrow that helps stablise the hip joint
- long head of biceps tendon
- articular capsule
- acetabular labrum
- acetabular ligament
* *5. ligamentum teres**
The muscles that produce this movement are innervated by which nerve?
- sciatic
- common peroneal
- femoral
- tibial
- obturator

The muscles that produce this movement are innervated by which nerve?
- sciatic
* *2. common peroneal** - femoral
- tibial
- obturator
The functions of area B include:
- Control of mastication and facial expression
- Processing discriminative touch sensation from the limbs
- Control of visual and auditory reflexes and conjugate eye movements
- Control of tongue movements, swallowing, coughing and vomiting
- Regulating cortical arousal and sleep wake cycles
The functions of area B include:
- Control of mastication and facial expression
- Processing discriminative touch sensation from the limbs
- Control of visual and auditory reflexes and conjugate eye movements
4. Control of tongue movements, swallowing, coughing and vomiting
5. Regulating cortical arousal and sleep wake cycles

- CT
- MRI
- Myelogram
- Angiogram
- Ventriculogram

- CT
- MRI
3. Myelogram - Angiogram
5. Ventriculogram
what type of tissue is this?
dense irregular fibrocollagenous tissue
2. dense regular fibrocollagenous tissue
3 compact bone
4. cancellous bone
5. hyaline cartilage

what type of tissue is this?
dense irregular fibrocollagenous tissue
2. dense regular fibrocollagenous tissue
3 compact bone
4. cancellous bone
5. hyaline cartilage
The preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system are located in this section.
A
B
C
D

The preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system are located in this section.
A
B
C
D
sympathetic action of this would cause pupil dilation
A
B
C
D
E
F

sympathetic action of this would cause pupil dilation
A
B
C
D
E
F
what is A?
- ciliary
ganglion - Edinger
Westphal
nucleus - pretectal
nucleus - sympathetic
ganglion - medial
vestibular
nucleus - oculomotor
nucleus

what is A?
- ciliary
ganglion
2. Edinger
Westphal
nucleus
- pretectal
nucleus - sympathetic
ganglion - medial
vestibular
nucleus - oculomotor
nucleus
which is the highlighted nerve?
- Optic
- Ophthalmic division of the trigeminal
- Troclear
- Abducens
- Oculomotor

which is the highlighted nerve?
- Optic
2. Ophthalmic division of the trigeminal
3. Troclear - Abducens
- Oculomotor

ID B
- F wave
- Stimulus
artefact - H wave
- M wave

ID B
1. F wave
2. Stimulus
artefact
3. H wave
4. M wave

damge to the blue arrow causes:
- Agraphia
- Expressive aphasia
- Loss of musical appreciation
- Alexia
- Conduction aphasia
- Receptive aphasia
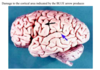
damge to the blue arrow causes:
1. Agraphia
- Expressive aphasia
- Loss of musical appreciation
- Alexia
- Conduction aphasia
* *6. Receptive aphasia**
ID H
- Basal ganglion
- Midbrain
- Thalamus
- Pineal gland
- Hypothalamus
- Fornix
- Pons

ID H
- Basal ganglion
- Midbrain
* *3. Thalamus** - Pineal gland
- Hypothalamus
- Fornix
- Pons
what is A?
- extensor pollicis longus
- abductor pollicis longus
- flexor pollicis longus
- abductor pollicic brevis
- extensor pollicis brevis

what is A?
- extensor pollicis longus
- abductor pollicis longus
- flexor pollicis longus
- abductor pollicic brevis
- extensor pollicis brevis
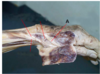
Which spinal curve is exaggerated in this woman?
- lumbar lordosis
- sacral kyphosis
- thoracic kyphosis
- cervical lordosis

Which spinal curve is exaggerated in this woman?
- *1. lumbar lordosis**
2. sacral kyphosis
3. thoracic kyphosis
4. cervical lordosis
what is 10?
- Tibiotalar ligament
- tendon of tibialis anterior
- spring ligament
- Deltoid ligaments of the ankle
- calcaneal tendon

what is 10?
- Tibiotalar ligament
- tendon of tibialis anterior
3. spring ligament - Deltoid ligaments of the ankle
- calcaneal tendon
what is a
- synovial fluid
- nucleus pulposus
- bone
- epiphyseal growth plate
- annulus fibrosus

what is a
- synovial fluid
* *2. nucleus pulposus** - bone
- epiphyseal growth plate
- annulus fibrosus