STEEPLECHASE - Parasites Flashcards
(98 cards)

Nymph

Sarcoptes - burrowing mite

Psoroptes - non-burrowing mite (e.g. Psoroptes ovis)
Sarcoptes scabiei - burrowing mite

Sarcoptic mange - burrowing mite

Demodex - burrowing mite

Demodecosis/demodectic mange

Psoroptes spp. (e.g. ovis)/sheep scab - non-burrowing mite


Chorioptes spp. (e.g. bovis) - non-burrowing mite

Otodectes cynotis - non-burrowing mite

Cheyletiella spp. - non-burrowing mite

Dermanyssus spp. - non-burrowing mite

Soft tick e.g. Argas spp. of birds

Hard tick e.g. Ixodes ricinus (castor bean tick in sheep) or Ioxdes hexagonous (hedgehogs)
Transmit babesiosis, Borrelia (Lyme disease), tick pyaemia, ehrlichiosis

Questioning hard tick (Ixodidae), waiting for host e.g. Ixodes ricinus (castor bean tick in sheep) or Ioxdes hexagonous (hedgehogs)
Transmit babesiosis, Borrelia (Lyme disease), tick pyaemia, ehrlichiosis

Engorged tick

Larva tick

Nymph tick

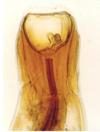
Haemonchus contortus (nematode), female “barber’s pole” appearance
Sheep - haemonchosis, absomasum, obtain blood from mucosal vessels before final moult
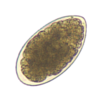
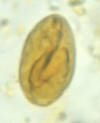
Strongyle egg, 80 micrometres (Nematodirus battus egg ~ 160 micrometres long)
E.g. Trichostrongylus axei (Sheep abomasum), Trichostrongylus spp. (Sheep small intestine), egg and L3 survive in environment under adverse conditions
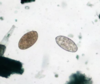
Rumen fluke (trematode) eggs e.g. Calicophoron daubneyi
Immature in duodenum, adults in forestomachs

Adult rumen fluke e.g. Calicophoron daubneyi

Galba truncatula - intermediate host of rumen fluke e.g. Calicophoron daubneyi, and liver fluke e.g. Fasciola hepatica
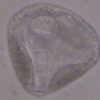
Moniezia benedeni/Moniezia expansa egg
Cestode parasite, adults in SI, calves & lambs, intermediate host = oribatid mite, solid mass of tapeworm could occlude intestinal lumen