The Hand Flashcards
(85 cards)
__ carpal bones
8
____ metacarpals
5
____ bones of the fingers
14
Most commonly fractured carpal bone
scaphoid
Scaphoid/lunate fractures can (in some individuals) disrupt the blood supply to the bone resulting in delayed or “non-union” (avascular necrosis) of the bone…often requiring surgical intervention
scaphoid
_____…most commonly dislocated carpal bone
Lunate
1st carpometacarpal joint is between the trapezium and the base of the 1st metacarpal. Common synovial joint to be affected by ____
arthritis
Known as “boxers fracture”- often seen following altercations in unskilled fighters
nFractures of the 5th metacarpal neck are commonly seen in emergency rooms “pinky”
nPalmar aponeurosis sends a medial septum to the ____ metacarpal
5th
nPalmar aponeurosis sends a lateral septum to the____ metacarpal
3rd
nThese septum divide the hand into five muscular compartments:
- Hypothenar
- Thenar
- Central
- Adductor
- Interosseous
nThese compartments are of clinical important because
they can limit the spread of infection within the hand
Base of the palmar aponeurosis sends ___ longitudinal fibrous slips which surround fibrous digital sheaths within the fingers
4
Trigger Finger
Trauma to tendons can result in scar tissue forming about a flexor tendon
Scarring creates a nodule on the tendon
Nodule catches/entraps beneath the annular ligaments of the fibrous sheath
This sometimes causes the finger to lock in position of flexion
With extension-the nodule slides beneath the ligament and releases- can be painful
Inflammation of the Synovial Tendon Sheaths is referred to as ____
tenosynovitis
______ are tubular “envelopes” containing synovial membrane/fluid that surround the tendons
These sheaths permit tendons to move freely with less friction during hand movements
Synovial Tendon Sheaths
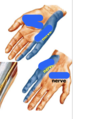
_____ located medially and contains 3 intrinsic muscles involved in moving the 5th digit (little finger)
Hypothenar Compartment
nHypothenar Compartment- located medially and contains 3 intrinsic muscles involved in moving the 5th digit (little finger)
- Abductor Digiti Minimi
- Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis
- Opponens Digiti Minimi
hypothenar compartment is innervated by
All Innervated by the deep branch of the ulnar nerve (C8 & T1)
_____ located laterally and mainly responsible for opposition of the thumb- also contains 3 intrinsic muscles
Thenar Compartment
3 muscles of the thenar compartment
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis* (contains a small sesamoid bone within its tendon)
- Opponens Pollicis
thenar compartment innervated by
All innervated by the recurrent branch of the median nerve (C8 & T1)
____ located deep within hand and responsible for adduction of the thumb- only one intrinsic muscle
Adductor Compartment
muscle of the adductor compartment
Adductor Pollicis- fan-shaped muscle with two heads of origin (transverse & oblique)
(contains a small sesamoid bone within its tendon)