Upper Limb Nerve Lesions Flashcards
(40 cards)
what are the root nerves for the long thoarcic nerve? What does it innervate?
C5 C6 C7 reach your arm up to heaven; anterior serratus
if the long thoarcic nerve C567 is damaged
winged scapula and the patient has difficulty raising the arm above the head; decreased medial rotation of the scapula










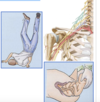
upper brachial plexus damage (C5 and C6)
Upper brachial plexus injuries are called _____
Erb’s- Palsy or Erb’s- Duchenne Palsy

Erb-Duchenne Palsy; Resulting limb is adducted, internally rotated, pronated and extended at the elbow

Lower brachial plexus injuries typically results from upper limb being suddenly pulled superiorly…grasping a limb during a fall or breech birth
This type of trauma can stretch or avulse C8 & T1 (sometimes C7) ventral rami (lower roots)
Lower brachial plexus lesions are referred to as ____
Klumpke Palsy
klumpkes or erbs palsy is more common?
erbs palsy (upper brachial plexus lesions/damage)









suprascapular nerve roots
C5 C6
If roots C5 and C6 are damaged
supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles are not innervated and cannot laterally move scapula; weak abduction = weakened supraspinatus
thoracodorsal nerve roots
C 678
if thoracodorsal nerve is damaged
decreased innervation of latissimus = decreased rowing climbing and pushing up out of a chair; decreased extension, adduction, and medially rotating arm
axillary nerve roots
C5 and C6
axillary nerve innervates
nInnervates the deltoid and teres minor


