Topic 8 Revision Questions + some study guide Flashcards
(38 cards)
Which nerve innervates muscles of mastication and the tensor veli palatini, and communicates sensation from the face, mouth, theeth, mucosal lining and tongue?

V - Trigeminal nerve.
3 branches:
V1- Opthalmic branch,
V2 Maxillary branch
V3 Mandibular branch
Which cranial nerve innervates muscles of facial expression and sensory to anterior 2/3 of the tongue?

VII - Facial Nerve
Which cranial nerve transmits auditory and balance sensations?
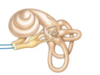
VIII - Vestibulocochlear
Which nerve serves the posterior tongue taste receptors, somatic sense from the tongue, fauces, pharynx, and Eustachian tube?

IX - glossopharyngeal nerve
Which nerve transmits:
Somatic sensation of pain, touch and temperature from the region of the ear drum, as well as pain sense from pharynx, larynx, esophagus and many other regions.
Motor innervation for the intrinsic muscles of the larynx:

X - Vagus nerve
Which cranial nerve innervates the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles, and collaborates with the vagus in the activation of palatal, laryngeal, and pharyngeal muscles?

XI - Accessory nerve
Which nerve innervates the muscles of the tongue with the exception of the palatoglossus?

XII Hypoglossal
Identify the sylomastoid foramen on this diagram, and which nerve passes through it.

VII - Facial

Identify the foramen ovale, and which nerve passes through it.

Foramen ovale
Trigeminal, mandibular branch V3

Identify the foramen magnum, and which cranial nerve passes through it.

Accessory nerve XI
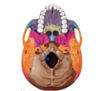
Identify the foramen indicated, and which cranial nerves pass through it.

Jugular foramen.
IX - Glossopharyngeal
X - Vagus
XI - Accessory
Identify the foramen indicated, and which cranial nerve passes through it.

Foramen rotundum
Trigeminal nerve, maxillary branch V2
Identify the foramen indicated, and which cranial nerve passes through it:
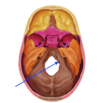
Hypoglossal Canal,
XII - Hypoglossal nerve
Identify the foramen indicated, and which cranial nerves pass through it:

Internal Auditory Meatus:
VII - Facial
VIII - Vestibulcochlear
Identify the foramen indicated, and which nerve passes through it:

Superior Orbital Fissure
Trigeminal nerve, opthalmic nerve V1
What would be the effects of lesions to CN V?
Damage to the whole nerve would cause loss of general sensation from that side of face, as well as paralysis of the TMJ muscles, mylohyoid, anterior digastric, tensor veli palatini and tensor tympani.
What would be the effects of damage to CN VII?
VII - Facial nerve
Muscles of facial expression would be paralysed, loss of taste sensation from anterior tongue. *
*technical nerve, whith some fibres crossing over. If question doesn’t specify where damage is, just assume it is after cross over. As a rule, there will not be technical questions in the exam about cross over.
What would be the effects of damage to CN IX?
IX - Glossopharyngeal
Loss of taste and general sensation from posteror tongue, loss of general sensation from middle ear, audotry tube, and pharynx, paralysis of stylophanryngeaus, parotid gland (so reduced saliva). All on same side as damaged nerve.
What would be the effects of damage to CN X?
X - Vagus nerve
- Loss of taste from root of tongue and epiglottis,
- loss of general and visceral sensation from inferior larynx, pharynx, thoracic and abdominal organs,
- some paralysis of muscles of soft palate, pharynx and intrinsic laryngeal muscles.
What would be the effects of damage to CN XI?
XI - Accessory nerve
Some paralysis of soft palate and pharynx muscles.
Which two foramina do CN VII pass through?
Stylomastoid foramen
Internal Auditory Meatus
When we say that a cranial nerve is ‘motor’ what does this mean?
Motor – this is information travelling from the CNS to muscles and some types of glands, and controls movement (and some glandular secretions). Motor nerves do not travel to any other types of tissues. Motor nerve fibres may be:
- Voluntary (somatic) motor – controlling voluntary movement of skeletal muscles;
- Involuntary (autonomic) motor – controlling movement of cardiac and smooth muscle, and some glands. The two subtypes of autonomic motor fibres are parasympathetic (control normal everyday function), and sympathetic (control stressful responses).
What would be the effects of damage to CN XII?
XII - Hypoglossal
Paralysis of intrinsic and extrinsic tongue muscles, and thyrohyoid and geniohyoid muscles (all on same side as nerve damage).
Which cranial nerve carries genearl sensation from the tympanic membrane?
The glossopharyngeal nerve (IX) also senses blood pressure and chemistry changes in the carotid sinus. There is also a sensory branch called the tympanic nerve carrying general sensory information from the tympanic membrane.



