Urinary Flashcards
(40 cards)
Functions of the urinary system:
- __________________ homeostasis
- Excretion of _______________, and excess _______
- Production of hormones: _________ and ___________.
- Regulation of blood pressure with the _________________.
- Activation of ___________
- Water and electrolyte
- toxic metabolite waste products and excess water
- renin and erythropoietin
- Juxtaglomerular apparatus
- vitamin D
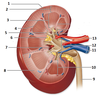
- Fibrous capsule
- Renal cortex
- Renal Medulla
- Corticomedullary junction
- Renal papilla
- Adipose tissue in renal sinus
- Renal sinus
- Renal lobe
- Ureter
- Renal pyramid
- Renal vein
- Renal pelvis
- Renal artery
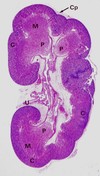
Cp – capsule
C – renal cortex
M – renal medulla
P – renal papilla
U – ureter
The functional unit of the kidney is the ________, and they are the site of osmoregulation via:
–___________ of small molecules from blood plasma to form a filtrate
–_______________ of most of the water and other molecules from the filtrate
Filtration
Selective reabsorption
The renal cortex contains what 6 structures?
- RENAL CORPUSCLES
- Proximal convoluted tubules
- Nephron loops (of Henle)
- Distal convoluted tubules
- Collecting tubules
- Peritubular capillary plexuses
The renal medulla contains what 3 things?
- Nephron loops of Henle
- Collecting ducts and vasa recta (straight arterioles)
- Interstitial cells
Main 2 parts of the renal corpuscle
Glomerulus
Glomerular capsule aka Bowman’s capsule
Cells of the visceral layer of the glomerular capsule
podocytes
cells of the parietal layer of the glomerular capsule
Squamous cells
___________ form fenestrated glomerular capillaries
endothelial cells
________ cells are between the fenestrated capillaries
Mesangial cells
In section the _______ are a distinctive feature of kidney cortex
Renal corpuscles
The long processes as foot projections called ________, of the ________ wrap around the capillaries, and leave slits between them. Blood is filtered through these slits, each known as a ____________.
pedicels
podocytes
filtration slit
___________ capillaries allow ______ sized molecules in blood to pass from the glomerular capillary into the urinary space of the renal corpuscle. Formed elements, _______ and molecules ______ than this remain in blood.
fenestrated
smaller
albumin
larger
_________ enters the tubular system via the urinary pole
Filtrate
Some molecules are __________ and _________ to the blood of the peritubular plexus and vasa recta
reabsorbed
returned
Primary/glomerular filtrate is produced by ultrafiltration of blood in the ____________. The composition of ultrafiltrate is similar to blood plasma, it does not contain _______.
renal corpuscle
proteins
What is reabsored in the proximal convoluted tubules?
water
most of Na+
all glucose
all amino acids
It is the tubular secretion of ______and _______ from the blood into the tubular fluid that helps to keep blood pH at its normal level. ______ is also secreted.
H+ (hydrogen) and NH4+ (ammonium)
K+ (Potassium)
Numerous pores – fenestrations in the _________ of the ____________ enable the passage of all the non-cellular elements of blood.
Endothelium of the glomerular capillary
The ______________ is a fused basal laminae of capillaries and podocytes serve as a glomerular ultrafilter. Albumin (m. w. 68,000) & larger molecules are retained; all smaller molecules cross freely through this filter.
glomerular basement membrane
___________ with their inter-digitating trabeculae and _______ form slit pores between processes, and the _________ part of Bowman’s capsule.
Podocytes
pedicles
visceral
___________ cells are contractile phagocytic cells that have receptors for ___________ and _________. They provide some structural support to the capillaries as well.
Mesangial cells
Angiotensin II and Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)
Glomerular Filtrate Pathway
- Urinary space of Bowman’s capsule
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Nephron loop
- Distal convoluted tubule
- Collecting and papillary duct
- Calyx or renal pelvis


