Visualizing cells Flashcards
(41 cards)
What wavelengths are contained by a white light source?
All of the wavelengths of visible light.
Which lens provides resolution to light microscopes?
The objective lens
What sets the resolution limit for a light microscope?
The wavelength of visible light.
d(resolution) = wavelength/ (objective + condenser)
Define resolving power.
The ability to distinguish between two distinct light sources as two distinct light sources.
What structure provides the majority of magnification for a light microscope?
The objective.
What are the two basic types of light microscope, and what is each good for?
- inverted microscope: for tissue culture dishes, bottles. The objective is below the sample, has a longer working distance
- upright microscope: used for slides (fixed or live samples). objectives are above sample, providing shorter working distance.
Describe the two types of iight paths.
- trans-illumination light path: incadescent light
- epi-ilumination light path: fluorescent light
What type of light uses a dichroic mirror?
Fluorescent light path
Describe the objective specs for a light microscope.
- application
- magnification
- numerical apperture: enhances resolution, gets higher as magnification increases
- field of view
- immersion medium: enhances resolution by using different medium than air to have higher resolution and to support a higher numerical apperture.
- lens quality: achromatic, apochromatic, plan, semi-plan

Describe the four types of lens quality for a light microscope.
Different numbers of lenses, lens coatings, and types of glass
- achromatic: corrected lens to bring two wavelengths into focus in same plane. Consists of two elements
- apochromatic: has better correction of chromatic and spherical abberation. Consists of three elements.
- semi-plan objective: 90% of total lens area gets high resolution image.
- plan/planar objective: more lenses, more expensive, more correction. This is the most desirable lens quality
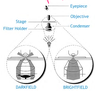
Describe the three manipulations of the light path in a light microscope.
- phase contrast: series of condensers and phase rings let only lateral light pass to eyepiece. provides enhanced contrast.
- darkfield: filter blocks out center field light so only edge of light reaches the sample. good for high contrast.
- brightfield (standard): all light reaches same focal plane where the sample sits.
- differential interference contrast: can be independently adjusted to vary the contrast of a specific subject while viewing it.
Describe cell and tissue preparation for light microscopy.
non-iving cells = more detail:
- crosslink cells or tissue in order to stain (methanol, paraformaldehyde, formalin, glutaraldehyde, osmium tetroxide)
- embed tissue in matrix (plastic, paraffin, or frozen embedding medium)
- section tissue (microtome, cryostat, sliding microtome, vibratome, or ultramicrotome)
- mount on slide
- visualize (histological stain, immunostain, inherent chromogen)
List some of the ways tissue can be stained.
- histologically
- antibodies
- tracers
- genetically modified tissues
Describe histological staining of a tissue.
hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining:
- hematoxylin stains negative
- eosin stains positive
- merging them provides a look at structures of fixed tissues

Describe myelin tissue staining.
stains proteins associated with myelin, not the myelin itself
Describe nissel staining.
stains DNA and RNA, and the rough ER (everything associated with the nucleus)
Describe the unlabelled antibody method of immunohistochemistry.
- provides more detail than H&E staining
- good for bright field imaging
1. primary antibody and biotinylated secondary antibody bind target molecule
2. avidin/biotinylated enzyme complex binds secondary antibody
3. enzyme substrate is added, which elicits a detectable response.

Describe the use of tracers as a light microscopy method.
Tracers get injected into a system, and get transported and localized. Great for dark field optics.
Describe the dichroic light filter.
it is a mirror which helps filter light for fluorescent light microscopy. it helps to filter a specific wavelength of light onto a sample, which if excited by that wavelength, will emit a wavelength of light lower in energy, which is observable through the lens or camera.

How can the 5 reliable fluorescent channels be used simultaneously for a sample?
They can all be introduced separately with different filter sets. This is made possible when there is minimal overlap in the wavelengths of the fluorophores being emmitted.
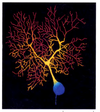
Describe traditional immunofluorescence.
- Highly sensitive method.
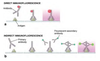
- direct immunofluorescence has fluorescent primary antibody. Is very specific, but not very intense
- indirect immunofluorescence consists of a primary antibody and fluorescent secondary antibody. More intense because multiple secondaries can bind a primary, and therefore there is higher resolution than direct immunofluorescence.
Describe the autoradiography light microscopy method.
A radioactive material such as thymidine is incorporated into a dividing cell’s DNA. Can then see where cells are localized and can count how many there are.
How are multicolor fluorescent images obtained?
different fluorescence filters are used to identify different molecules/structures. these images are taken in grayscale. a computer then merges them together and adds color.

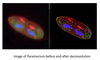
Describe optical sectioning and deconvolution microscopy.
It scans up and down a sample, taking cross sectional images, then reconstructs them in 3D. It allows us to understand the spatial organization of organelles and how they relate to one another. Can also enhance the resolution of these images with computer technology (deconvolution) which gets rid of haziness by replacing hazy pixels in one cross section with clear pixels from another.