Week 1 Flashcards
(192 cards)
How muscle can be affected after neural fibers are removed from the muscle?
Muscle atrophy
What is Spondylolisthesis?
Displacement of vertebra
What degeneration of cartilage between bones might lead to?
More bone rubbing leading to bone growth
Which part of vertebra are fused?
Coccygeal
Which vertebra do not have the intervertebral disk?
Atlas and axis
How many cervical nerves are there?
How many cervical vertebra are there?
8
7
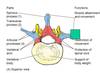
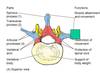
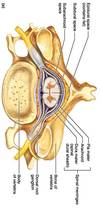
What is the name of the hole that spinal cord is passing through?
Vertebral foramen
What forms neural arch?
Pedicle
Lamina
Body
What is the join between inferior and superior transverse proceeses of vertebra
azygoshypophyseal joint
Name the locations where nerves are exiting from spinal cord
Intravertebral foramen
What is the effect of anastetic injected in sacral hiatus?
Only affects spinal nerves not spinal cord
What artery passes through transverse foramen of cervical vertebra?
Exception?
Vertebral artery C1-6 not 7
Which vertebra can be felt on the back of the neck?
C7
What articular facets are connected to?
Which type of vertebra are they found in?
Ribs
Thoracic
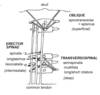
Direction of superior/inferior articular proceses:
Cervical vertebra
Thoracic vertebra
Lumbar vertebra
Transverse plane
Frontal plane
Saggital plane
Would thicker or thinker disc allow more movement?
Thicker
What is found in all vertebra except atlas?
Body
What is the difference in shape of inferior vs. superior articular fovea?
What movement is allowed by superior articular fovea?
Superior is more concave
Front/back
Why spinal cord does not extend entire length of vertebral column?
It does not grow as much as vertrebral column
What is the special innervation of trapeizus muscle?
Innervated by CN XI
What is osteophytes?
a bony outgrowth associated with the degeneration of cartilage at joints
Components of axial skeleton
Skull
Vertebral column
Ribs
Sternum (not pelvis)
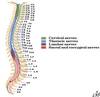
How many vertebra are there?
How many at each level?
7C, 12T, 5L, 5S, 4C

Which segment of vertebral colum belong to primary / secondary curvatures
Primary: thoracic & sacral
Secondary: cervical & lumbar