Week 2 Flashcards
(171 cards)
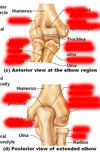
Scapula label


Where is scapula connected to clavicle?
What does it form with clavicle?
Acromion
Shoulder gridle
What is special about clavicle with respect to the development?
What is the orgin?
First long bone to ossify wk5-6 and last one to fuse 25 yo
membranous origin

Two joints of clavicle
Sternoclavicular joint
Acromioclavicular joint
What is one structure that connects arm to the axial skeleton?
Clavicle
Label ligaments


Where does the shoulder separation occur?
WHere does the shoulder dislocation occur?
Where does the clavicle break most often?
AC joint
glenohumeral joint
Middle/lateral thirds
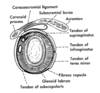
What is unusal about Strenoclavicular joint
What is the disc made of?
Two bursas separated by articular disc
Fibrocartilage

Movements of the Sternoclavicular Joint
Axis? Movement
Vertical axis —– protraction/retraction
AP axis —– elevation/depression
Oblique axis —– medial/lateral rotation

How much degree of abduction occurs at glenohumeral joint?
How much occurs at sternoclavicular joint?
What is the name of this movement?
120
60
scapulohumeral rhythm
Movements of the Trapezius
Verical axis?
AP axis?
Oblique axis?
Retract
(Superior) elevates (Infectior) depresses
Rotate

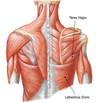
Trapezius Muscle
Nerve supply
Spinal accessory nerve (XI) Supplies motor
Cervical segments C3 & C4 Supply proprioceptive
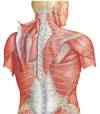
Latissimus Dorsi
Direction of movement?
Nerve supply?
Connects between?
Adduction / Extension
Thoracodorsal nerve (middle subscapular)
Thoracolumbar fascia to humerus

Superficial (extrinsic) Back Muscles
Movement?
Nerve?
Medially rotate scapula
Dorsal Scapular nerve

Levator scapula
Movement?
Nerve?
Elevates and medially rotates scapula
Dorsal Scapular

Pectoralis Minor
Movememnts?
Nerve?
Medial Pectoral Nerve
Depresses, Protracts, Medially Rotates
Serratus Anterior
Movement? Structural importance?
Innervation?
Depression, protraction, lateral rotation
Holding medial border of scapula close to ribs
Lorng Thoracic Nerve

What is winging
Loss of serratus anterior function e.g. loss of the neve

Muscles of the SC-joint
Protraction
Retraction?
Elevation?
Depression?
Medial rotation?
Lateral rotation?

Movements of glenohumeral joint
Horizontal transverse axis —– flexion/extension
Horizontal AP axis —– abduction/adduction
Vertical axis —– rotation

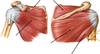
Structures protecting muscle around Glenohumeral joint
Subdeltoid bursa
Subacromial bursa
Biceps brachii tendon

Pectoralis Major
Nerve?
Movement?
Medial and Lateral Pectoral
Flexion, Adduction, medial rotation

Deltoid
Movement?
Innervation?
Axillary
Flexion: Anterior
Extension: Posterior
Abduction: Middle
Adduction: Posterior and Anterior
Medial Rotation: Anterior
Lateral Rotation: Posterior

Teres Major
Innervation?
Middle Subscapular or thoracodorsal (Latissimus)
Lower Subscapular (Teres)
Extension
Adduction
Medial Rotation