Week 3 Flashcards
(151 cards)
Groups of anteiror arm muscle
Thenar
Hypothenar
Lumbricals
Interossei
List thenar muscle
List hypothenar muscle
Innervation?
Thenar muscles - median
Opponens pollicis
Abductor pollicis brevis
Flexor pollicis brevis
Hypothenar muscles - ulnar
Opponens digiti minimi
Abductor digiti minimi
Flexor digiti minimi (brevis)
Ulnar nerve
What passes through the carpal tunnel
Medial nerve
Flexor pollicus longus
Flexor digitorum superficialis
Flexor digitorum profundus
Name the compartments


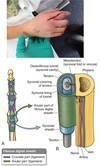
Dupuytren’s Contracture
A disease of the palmar fascia resulting in thickening and shortening of fibrous bands on the palmar surface of the hand and fingers.

Arrangement of tendon sheats in palm
thenar (2)
midpalmar (3+4)

Fibrous Digital Sheaths
Attachement and their location?
Importance?
Bands A2 and A4 are on the proximal and middle phalanx respectively
A1,A3, and A5 are near the MP, PIP and DIP respectively
A2 and A4 Bands are most important to prevent bowstringing. A1 band is involved in trigger finger.

Lumbirical muscles
Origin?
Insertion?
Innervation?
Function
Originate from the flexor digitorum profundus tendons
Insert in the extensor hoods
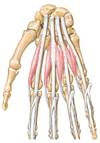
Interosseus Muscle
2 types?
Function
Origin?
Insertion?
Innervation
Dorsal and palmar
Originate from metacarpals
Insert on the extensor hoods
PaD / DaB
Ulnar

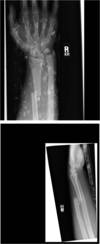
Fracture of Scapoid
Complications?
Most common wrist fracture
Non-union
Avascular necrosis

Dermatomes in the upper limb

Cutaneous Innervation of the Upper Limb
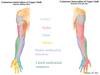
Segmental Innervation of the Upper Limb

Innervation to
Anterior arm?
Anterior forearm?
Shoulder?
Posterior arm?
Posterior forearm?
Anterior compartment
anterior arm-musculocutaneous
anterior forearm-all median except FCU+2 heads of FDP (ulnar)
anterior hand-all ulnar except thenar comp muscles + lumbricals to the functional midline on radial side (median)
Posterior compartment
Shoulder-axillary (deltoid and teres minor)
posterior arm & forearm-radial
Erb-Duchenne Paralysis
Cause?
Symptoms?
Damage to upper trunk of the brachial plexus
Shoulder movements are affected most dramatically

Klumpke’s Paralysis
Cause?
Symptoms?
Damage of lower trunk of the brachial plexus
Hand movements are affected most dramatically

Damage to
Axillary?
Musculocutaneous?
Radial?
Axillary nerve-severely weakened abduction, weakened lateral rotation
Musculocutaneous nerve- almost no forearm flexion, weakened arm flexion
Radial nerve-no forearm extension, arm may be slightly flexed
(note also has major effect on forearm and hand, see later)
Mid humeral shaft fracture damage to what?
Radial Nerve
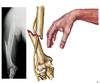
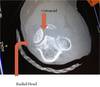
Elbow fracture damage to what?
Median Nerve Damage

Ulnar Nerve Damage
Location?
Phenotype?
Fracture of the medial epicondyle can cause trauma to the ulnar nerve.
Hyperextension with flexion

Jersey finger
Tendon injury Flexor Profundus vs. Superficialis?
Tear of the FDP off the distal phalanx
Profundus-passively extend MP and PIP while trying to flex the DIP
Superficialis-passively extend unaffected fingers while trying to flex

Extensor Tendon Injuries
Mallet finger?
Boutonniére deformity?

Axis of Rotation for Upper Limb Joints
- *Glenohumeral**-AP (ab and adduction), vertical (rotation), transverse (flex and extend)
- *Humeroulnar**-transverse (flex and extend)
- *Humeroradial**-transverse (flex and extend), vertical, rotation (pronate and supinate)
- *Radioulnar**-vertical, rotation (pronate supinate)
- *Radiocarpal**-transverse (flex and extend), AP (ab and adduct
Axis of rotation
Fingers?
Thumb?
Often arthiritis where?
Thumb
Carpometacarpal multiaxi
MP uniaxial
Finger
MP biaxial
1st CMC