Week 2: Upper Limbs & Back Flashcards
(31 cards)
What are the origin and insertion of a muscle?
Origin - attachment point that does not move during contraction of the muscle
Insertion - attachment point that does move during the contraction of the muscle
When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin

What organizes limbs into compartment?
Deep fascia and connective tissue wraps muscles into compartments that have their own nerves and blood supplies

What are the main components of the upper and lower limb?
Upper:
Axilla, arm, forearm (ant/post compartments), hand
Lower:
Gluteal region, thigh (ant/post/medial compartments), leg (ant/post/lat compartments), foot
What are the three main groups of back muscles?
Superficial, intermediate, and deep (intrinsic)
What are the superficial muscles of the back, what do they do, and what are they innervated by?
Latissimus dorsi, rhomboids, trapezius and levator scapulae all assist in movement of the upper limb
These are innervated by the brachial plexus, except for the trapezius muscle, which is innervated by CN XI

What are the deep muscles of the back, what do they do and what are they innervated by?
The deep/intrinsic muscles are the erector spinae and transversospinalis. They are involved in stabilizing and moving the trunk.
They are innervated by the dorsal rami of the spinal nerves.

Label A-E

A - Trapezius
B - Latissimus dorsi
C - Levator scapulae
D - Rhomboid minor
E - Rhomboid major

What are the three main muscle movements of the trapezius?
Elevation (shrug up)
Depression (shrug down)
Retraction (pull towards the back)
What are the main movements of the latissimus dorsi?
“Swimming” movements of the shoulder/upper humerus of the arm:
extension towards the back
adduction towards the midline
medial rotation of the insertion point
What are the main movements of the rhomboid major and minor?
Retraction of the scapulae torwards the back
Elevation of scapula (“shrug” movement)
What two muscles would be involved in “flapping” your arms like a bird?
Supraspinatus initiates the first 15 degrees of movement
Deltoid muscle allows for arm abduction beyond 15 degrees

What are the main rotator cuff muscles and what do they do?
These are the muscles around the scapula that rotate, abduct and stabilize the shoulder
The infraspinatus(post) allows forlateralrotation(moves shoulder towards the back). Thesupraspinatus (superior) allows for elevation and resists the downward pull of gravity
Teres minor (post) also allows for lateral rotation
Subscapularis is on the anterior side and allows for medial rotation (towards the anterior midline)

The ______________ joint is between the shoulder and humerus. What is unique about it?
Glenohumeral. It is a socket-like joint that doesn’t actually have much of a “socket,” so it depends on the muscles and ligaments of the rotator cuffs to hold it in place.
What are the main contents of the axilla, and why is it important?
Axillary area is where structures pass from the neck to the upper thorax (i.e. nerves, veins, arteries)
Contents:
Axillary artery/vein
Brachial plexus
Lymphatics and lymph nodes
The __________ _____________ starts within the ________ and carries the nerves for the skin and muscles of the upper limb and shoulder. What do these nerves form from?
Brachial plexus
Neck
Nerves form from the anterior rami of the C5 - T1 spinal segments
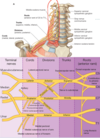
From proximal to distal, what is the organization of nerves deriving from the brachial plexus?
“Road To DC Baby”
Proximal:
Roots (ventral/anterior rami, C5-8, T1)
Trunks (superior (C5,6), middle (C7), inferior (C8, T1)
Divisions (anterior and posterior parts of arm)
Cords (lateral, posterior, medial)
Branches (terminal nerves
Distal

What are the four terminal nerves of the brachial plexus and what does each do?
Musculocutaneous - Anterior arm compartment
Median - Forearm: most anterior compartment (except those innervated by ulnar nerve), and Hand: thenar eminence and 2 other muscles + skin of hand
Ulnar - Forearm: 1.5 muscles, and Hand: all intrinsic muscles except those innervated by median nerve, skin of hand
Radial - Posterior compartment of arm and forearm, skin over posterior

What three nerves are responsible for the cutaneous innervation of the hand?
Median (lateral palm, fingers)
ulnar (median palm, medial 1.5 fingers)
and radial nerves (posterior lateral part of hand)

What is the “M” of the brachial plexus?
Lateral to medial:
Musculocutaneous
Median
Ulnar
(Radial nerve is behind the axillary artery)
How can you injure elements of the brachial plexus, and what nerves are involved in injury?
Upper brachial injury is caused by damage to the neck like lateral overstretching, which damages C5 & C6
Lower brachial injury is caused by damage to the axillary region from pulling trauma, which damages C8 and T1

What are the major compartments of the arm, what muscles do they contain, what common actions do they commit and how are they innervated?
Compartments are anterior and posterior
Anterior contains the biceps brachii, which is the flexor compartment and is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve
Posterior contains the triceps brachii, which is the extensor compartment and is innervated by the radial nerve

What are the muscles of the anterior arm, what do they do and where do they originate and insert?
The three biceps brachii are the load-bearing flexors and supinators of the forearm.
They originate in the scapula and proximal humerus and insert in the radius, pulling it across the ulna to pronate the hand (ulna is medial)

What are the muscles of the posterior arm, what do they do and where do they originate and insert? What innervates it?
The three triceps brachii originate from the scapula (1) and humerus (2) and insert on the posterior ulna
They activate extension of the elbow, which is mediated by the radial nerve

What is the cubital fossa and what does it contain?
It is the depression anterior to the elbow joint that contains:
Tendons of biceps muscle
Median nerve
Brachial artery
It also contains the superficial veins used for venipuncture









