Week 3 Flashcards
(142 cards)
How are hormones released (pathways) into the anterior pituitary and the posterior pituitary?
- Anterior pituitary – releasing hormones released into blood supply from hypothalamus → travel to Ant. Pituitary → releases another hormone into the body
- Posterior pituitary – nerves from hypothalamus release releasing hormone directly to central blood supply
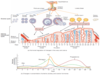
What hormones go through the anterior and posterior? Diagram.

What are the 4 types of proteins?
AA derivatives, steroids, peptides, proteins
What are the two amino acids that hormones are derived from? What hormones are derived from each?
- Amino Acid Derivatives
- Tyrosine → catecholamines
- Tryptophan → serotonin and melatonin
Name 6 steroid hormones and what they are dervied from?
- Steroids
- Derived from cholesterol → progesterone, androgens, testosterone, aldosterone, cortisol
- Vitamin D: 7-dehyrocholesterol → cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3) via sunlight
What are three drug types that modulate steroids hormones? What are their MOAs?? What can these be used for?
- Pharmacology
- Tamoxifen/raloxifene – antiestrogens for ER-positive breast cancer
- Aminoglutethimide/Anastrazole – aromatase inhibitor, blocks estrogen synthesis
- Premenopausal women – estrogen synthesis in ovary
- Postmenopausal women – estrogen synthesis in adipose tissue
- Flutamide/Bicalutamide – antiandrogens useful for prostate cancer
Name some peptide hormones (4)
- Peptides – less than 50 amino acids
- TRH, oxytocin, ACTH, insulin
Name some protein hormones (4)
- Proteins
- FSH, LH, TSH, hCG – highly conserved 92 AA unit
Note that these 4 are VERY VERY SIMILAR
How are signals transduced from hormones? 3 pathways
Signal Transduction
- 7TM-GPCRs, Tyrosine kinases, Nuclear receptors
Define negative feedback and what it does in terms of hormone regulation.
Negative Feedback
- Tight regulation of “hormonal homeostasis” that maintains hormonal levels in a tight physiological range
Name two GnRH analogs and what they are used in. What are their MOAs?
- GnRH analogs
- Leuprolide/goserelin – used in prostate cancer
- MOA: analog binds → constant stimulation of ant. pituitary → desensitization → decreased testosterone/estrogen
- Leuprolide/goserelin – used in prostate cancer
Name 2 antiestorgens, 2 aromatase inhibitors, 2 antiandrogens?
- Tamoxifen/raloxifene – antiestrogens for ER-positive breast cancer
- Aminoglutethimide/Anastrazole – aromatase inhibitor, blocks estrogen synthesis
- Premenopausal women – estrogen synthesis in ovary
- Postmenopausal women – estrogen synthesis in adipose tissue
- Flutamide/Bicalutamide – antiandrogens useful for prostate cancer
Follicular phase
- What hormone is dominant?
- Is LH or FSH release more?
- What occurs to the endoemetrium?
- Follicular (Proliferation of the endometrial tissue) – estrogen dominant
- Increased pulsatile frequency of GnRH release favors LH release, but in lower concentrations
- Continuous release of a GnRH analogue → decreased release of LH, FSH
- Changes in endometrium
- Mitosis, thickening of stroma, growth of glands
- Increased pulsatile frequency of GnRH release favors LH release, but in lower concentrations
Luteal phase
- What hormone is dominant?
- Is LH or FSH release more?
- What occurs to the endoemetrium?
- Luteal (Secretions by endometrial tissue) – progesterone dominant
- Decreased pulsatile frequency of GnRH release favors FSH release, but in higher concentrations
- Changes in endometrium
- Secretion from glands, edematous stroma, growth of endometrium inhibited
What are the main steps in the ovarian cycle?
Primoridal follicles → recruitment → Follicular growth → selection of dominant follicle → ovulation → luteal phase → menstruation → pregnancy (if fertilized)
What happens to the primordial follicles at the beginning of the ovarian cycle?
- Primordial follicles – goes through cycles of growth and apoptosis independent of FSH/LH
What happens in the recruitment phase of the ovarian cycle? How many follicles are recruited? What hormones are low and high?
- Recruitment – FSH stimulates multiple (3 to 11) primordial follicles → primary follicles → antral (secondary) follicles
- At luteal-to-follicular transition, steroids (estrogen) and inhibin are low → high levels of FSH (high estrogen inhibits FSH release)
What happens in the follicular growth phase of the ovarian cycle? What cells are stumulated? What hormones are high?
- Follicular growth – Increasing FSH → stimulation of granulosa cells → increased estrogen (estradiol) → growth
- LH stimulates Theca cells → production of androgens/testosterone from cholesterol → granulosa cells convert androgens to estrogen via aromatase (high estrogen increases LH release)
What happens in the selection of dominant follicle phase of the ovarian cycle? When does it occur? What cells are stumulated? What hormones are high?
- Selection of the dominant follicle (cycle day 5 to 7) – estrogen/FSH induce FSH receptor expression on one of the developing follicle → granulosa proliferation → dominant follicle
- Also induces activation of VEGF → capillary bed formation (more blood flow) → more FSH reaches dominant follicle
- FSH also induces LH receptors on granulosa cells
What happens in the ovulation phase of the ovarian cycle? What is synthesized and what does this lead to? What happens to the follicle as a result?
- Ovulation – due to LH surge (can also be seen as an increase in temperature due to progesterone release)
- Synthesis of collagenases and prostaglandins → thinning of follicular wall and contraction of smooth muscle around follicle → dominant follicle ruptures and releases oocyte
- Remaining follicle → corpus luteum → production of progesterone and drop in estrogen
What happens in the luteal phase of the ovaian cycle? What is inhibited/activated? What occurs if there is no fertilization?
- Luteal phase (14 days)– the production of hormones (progesterone, estrogen, inhibin) by corpus luteum by LH stimulation
- Inhibin inhibits both FSH and LH
- If no fertilization, corpus luteum after 9 to 11 days → corpus albicans
What happens during the menstruation phase of the ovarian cycle? How long does it last? What are the hormone levels?
Does the follicular phase or luteal phase vary?
- Menstruation – last about 3 to 5 days
- Decrease in estrogen and progesterone levels → menstrual shedding of endometrium
- Cycle lengths vary due to variation in length of follicular phase
What occurs during pregnancy? Why do you not get menses (what happens to the hormones)?
- Pregnancy (fertilization of oocyte by sperm) – results in rescue of corpus luteum
- Production of Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) – molecule similar to LH
- Stimulates the corpus luteum to produce progesterone and estrogen
- No fall in E + P → No menses
- Production of Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) – molecule similar to LH
What is the cervix response to estrogen?
- Mucous production
- Estradiol
- Thin, watery mucous
- Glairy “raw egg white”
- Facilitates sperm progression
- Ferns on microscope slide
- Estradiol