Week 3 - Ch.9 & Ch.13 Flashcards
(110 cards)
what is subjective data vs objective data ?
Subjective is the patients own experiences
objective data is gathered through technical measurements and observations by healthcare providers
what is inspection vs palpation ?
Inspection is concentrated watching while palpation is used the sense of touch to confirm what you have seen during inspection
what is percussion ?
it is the tapping of the persons skin with short, sharp strokes to asses underlying structures
why use percussion when x-rays are available ?
your hands are easily available, immediate feedback
What are the two forms of percussions ?
1) Direct : striking hand contacts the patients body wall
2) indirect: in which the your non dominant striking is placed on the patient - your middle finger of that hand stays on the surface while the other fingers need to be lifted - with dominant hand use the middle finger to percuss the stationary middle finger on patients body - movement is all in the wrist
what characteristics in sound do you look for in the percussion process ?
amplitude (intensity - loudness - softness), pitch ( frequency - vibrations per second), quality (timbre) , overtone ( length of time the note lingers)
what are the basic differences in sounds that one should look for ?
structures with more air (lungs) produce louder, deeper, and longer sounds b/c it vibrates freely
denser structures (bones or organs) give softer, higher, shorter, sounds
what is auscultation ?
listening to parts of the body such as the heart and the blood vessels - this requires a stethoscope
What is a diaphragm and bell in a stethoscope ?
Diaphragm ( flat edge) that is used for hearing high pitched sounds such breathe, bowel, and normal high pitched sounds
Bell is best for soft low pitched sounds
do not listen through gown
what should be done prior to starting any assessment ?
An ENVIRONMENTAL SCAN needs to be done to assess any risks, both sides of patients body are open, no noises, lighting
What is a Otoscope ?
it funnels light into the ear canal and onto the tympanic membrane
what is a Ophthalmoscope ?
it illuminates the internal eye structure
What is important to do after the use of equipment
it is important to clean the equipment - make sure to have a designated clean and dirty area
Define health care associated infections ?
they are infections that are acquired in a health care setting - hospitals are reservoirs for virulent microorganisms some of which are antibiotic resistant
what are the steps needed to prevent HAI’s ?
1) before initial patient or patient environment contact 2) before sceptic procedures 3) after contact with blood, bodily fluids, secretions, excretions 4) after contact with any equipment contaminated with body fluids 5) after removing gloves
what are the tiers of precautions ?
1) Routine practices - which are intended to be used for all patients at all times - regardless of their risk of infection - these practices are designed to reduce the risk of transmission of microorganisms - they apply to all excretions except sweat
2) Additional precautions - which are intended to be used when routine practices cannot fully manage the transmission of organisms
how do you handle assessment with a infant ?
make sure that the parent is present - place supine on padded examination table - perform examination 1 to 2 hours after child has been fed - make sure environment is warm - most infants like eye contact -
how do you handle assessment with a toddler ?
have the child sit up - greet the child - have mother or parent undress child - start with non threatening areas - head, nose, ears, or throat last
how do you handle assessment with preschool age children ?
verbal communication is good - offer choice if possible - allow them to pay with equipment if it helps - examine thorax, abdomen, extremities, and genitalia - head, eye, nose, ear, throat last
how do you handle assessment with school age children ?
they can sit on examination table - small talk is good to break the ice - children should undress on their own (leave pants on, gown , or cover with towel) - head to toe approach
how do you handle assessment with adolescents ?
adolescent should be alone without parent or sibling -do not treat them like an adult or a child - examine genatalia last - head to toe approach
How do you perform assessment on older adults ?
place on examining table - use sense of touch b/c other senses may be diminishing - head to toe approach
how do you perform assessment when individuals have acute challenges ?
Collecting a mini database of the problem and continuing examination when distress is alleviated
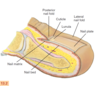
What are the layers of the skin ? In order, from outermost to innermost layer ?
epidermis - dermis- subcutaneous layer