Week 8 - Ch. 20 & 21 Flashcards
(121 cards)
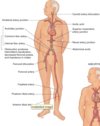
What does the cardiovascular system consist of ?
The heart
Blood vessels
What is the Precordium ?
The area of the anterior chest overlying the heart and great vessels
The great vessels are the major arteries and veins connected to the heart - the heart and the great vessels are located between the lungs in the middle third of the thoracic cage this area is called Mediastinum
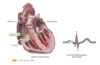
Where is the heart located ?
The heart extends from the levels of the second to the fifth inetcostal spaces
from the right border of the sternum to the left medicavicular line
What is the positioning of the hearts four ventricles ?
The right ventricle is immediately behind the sternum
The left ventricle lies behind the righ ventricle
The right atrium lies to the right and right above the right ventricle
The left ventricle is located posteriorly
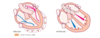
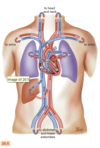
How are the blood vessels arranged ?
Blood vessels are arranged in two cotinous loops which are the pulmonary circulation and the systemic circulation
The top of the heart can be seen as the base and the bottom of the heart is the apex
The Great vessels lie bunched above the base of the heart

What is the apical pulse and where is it located ?
During the contraction, the apex beats against the chest wall that is the Apical Pulse which can be palpable as it is located at the fifth intercostal space
What are some aspects of the heart vessels and what are their features ?
The Superior Venae Cavae & Inferior Venae Cavae return unoxyegnated venous blood to the right side of the heart
The Pulmonary Artery leave the right ventricle, bifurcates, and carries the venous blood to the lungs
The Pulmonary Veins return the freshly oxyegnated blood to the left side of the heart
The Aorta carries out to the body - the aorta ascends from the left ventricle and descends behing the heart
What is the Heart Wall ? What are the layers of the heart ?
The Heart Wall has numerous layers:
- Pericardium: tough, fibrous, double walled sac taht surronds and protects the heartt - it contains two layers that contain a few ml of serous Pericardial fluid this allows smooth friction free movement of the heart muscle - the pericardium is anchored to the diagphragm
- Myocardium: is the muscular wall of the heartl it does the pumping
- Endocardium: is the thin layer of endothelial tissue that lines the inner surface of the heart chambers and valves
How is the heart divided ?
Right side of the heart pumps blood into the lung
Left side of the heart pumps blood into the body
The two sides of the heart are sepearated by the imperpeable wall called the Septum
The Artrium is the thin walled reservoir for holding blood and the thick walled Ventricle is musclar pumping chamber
What are valves ? how many are there ?
The four chambers are seperated by swinging door like structures called Valves - which is there to prevent the backflow of blood
Valves are unidirectional - they open and close passively in response to pressure gradients
There are four valves in the heart:
- Atrioventricular Valves (AV)* separtes atria and ventricles: there are two AV Valves Tricuspid Valve is the right AV valve and the Mitral Valve which is the left AV valve
- Semilunar Valves* are located between the ventricles and the pulmonary arteries: there are two semilunar valves - Pulmonic valve on the right side of the heart - Aortic Valve on the left side of the heart -( these valves open during systole to allow blood to be ejected from the heart)
What are the some aspects of valves ?
The valves are thin leaflets that are anchored by collagenous fibres called Chordae Tendineae - the thin leaflets are anchored to the papillary muscles embedded in the ventricle floor
The AV valves open during the filling phase (Diastole) - during the pumping phase (Systole) the AV valves close to prevent the reurgitation of blood back into the artria

What is an important thing to note about the heart ?
there are no valves between the venae cavae and the right atrium, nor between the pulmonary veins and the left atrium
For this reason, abnormally high pressure in the left side of the heart produces symptoms of pulmonary congestion, or heart failure, and abnormally high pressure in the right side of the heart manifests as distension of neck veins and abdomen
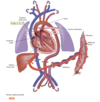
What is the direction of blood flow ?
- Blood flows from liver to right atrium through inferior
vena cava. Superior vena cava drains venous blood from the head and upper extremities. From right atrium, venous blood travels through tricuspid valve to right ventricle. - From right ventricle, venous blood flows through pulmonic valve to pulmonary artery. Pulmonary artery delivers unoxygenated blood to lungs.
- Lungs oxygenate blood. Pulmonary veins return fresh blood to left atrium.
- From left atrium, arterial blood travels through mitral valve to left ventricle. Left ventricle ejects blood through aortic valve into aorta.
- Aorta delivers oxygenated blood to body
Remember that the circulation is a continuous loop - The blood flows from an area of higher pressure to one of lower pressure
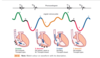
What is the Cardiac Cycle ?
The Cardiac Cycle is the rythmic movement of blood through the heart which has two phases the diastole and systole
What is Diastole ?
The ventricles are relaxed - the AV valves are open
The pressure in the atria are higher than that in the ventricles - so blood pours rapidly in the ventricles
The first passive filling is called Early or Protodiastolic Filling
Toward the end of diastole - the atria contracts and pushes the last amount of blood into the ventricles - this is active filling that is called Presystole or Atrial Systole - sometimes this called atrial kick becuase it causes a small rise in left ventricular pressure
What is important to note about Diastole ?
Atrial systole occurs during ventricular diastole, a confusing but important point
What is Systole ?
At the point of Systole a large vilume of blood has been pumped into the ventricles - this volume raises the ventricular pressure so it is higher than that in the atria
The Mitral and Tricupsid Valves swing shut
The closing of the AV valves contributes to the first heart nose (S1) and signals the beginning of systole
For a brief tme, all four valves are closed - the ventricular walls contract - this contraction in a closed system causes a build up pressure inside the ventricles - this is called Isometric Contraction
When the pressure in the ventricle finally exceeds pressure in the aorta, the aortic valve opens and blood is ejected rapidly
After the ventricle’s contents are ejected, its pressure falls - When pressure falls below pressure in the aorta, some blood flows backward toward the ventricle, causing the aortic valve to swing shut - This closure of the semilunar valves causes the second heart sound (S2) and signals the end of systole
What is ?Diastole Again”?
At this point all four valves are closed and the ventricles relax - this is called isometric or isovolumic relaxtion
At this time the atria is filling with blood delivered from the lungs - atrial pressure is higher than the relaxed ventricular pressure
The Mitral Valve drifts open and diastolic fillig begins again
What is happening in the right and left chambers ?
The same events occur in the right side of the heart and left side - the pressure in the right chambers are much lower than the pressure in the left chambers
This is because the left chambers require less energy to pump blood to the destinatio - this is pulmonary circulation
The events on the right side of the heart because of the route of myocardial depolarization
As a results, each of the heart sounds has two distinct components, and sometimes you can hear them separately - In S1, closure of the mitral valve (M1) can be heard just before tricuspid valve closure (T1) - In S2, aortic valve closure (A2) occurs slightly before pulmonic valve closure (P2)
What are normal heart sounds ?
The first heart sound (S1) occurs with the closure of the AV valves which signals the beginning of systole
The mitral component (M1) is slightlt before the Tricuspid (T1) component - These two compnents are heard as a fused sound
S1 is usually located at the Apex
What is the second Heart sound ?
The second heart sound (S2) occurs with the clsoure of the semilunar valves and signals the end of systole
The Aortic (A2) sound is slightly before the pulmonic component (P2)
S2 is loudest at the base
How does respiration affect systole ?
the volume of the left and right ventricular systole are usually balanced however they can be affected by respiration
The menomic to follow is:
moRe to the Right
Less to the Left
Explaine how resporation affects pressure in the heart ?
During inspiration, intrarthoric pressure is decreased - this pushes more blood into the Venae Cavae - increasing the venous return to the right side of the heart - this then increases the ventricular heart volume - this increased volume prolongs the right ventricular systole and delays pulmonic valve closure
On the left side - a greater amount of blood is sequestered at the lungs during inspiration - this for a moment decreases the amount of blood returned to the left side of the heart - this decreases the left ventricular stroke volume - this decrease in stroke volume shortens the left ventricular systole which allows the aortic valve to close early -
** when the aortic valve closes significantly earlier than the pulmonic valve. you heart two components - split S2 **

What are some extra heart sounds ?
Third Heart sound (S3)
Normally diastole is silent - however in some conditions ventricular filling causes vibrations that can be heard over the chest - these vibrations make the S3 sound
The S3 is heard when when the ventricles are resistant to filling during the early rapid filling phase (Protodiastole) - this occurs immediately after S2 when the AV valves open and the atrial blood pours into the ventricles
The Fourth heart sound (S4)
The S4 occurs at the end of diastole (at presystole) when the ventricle is resistant to swelling - the atria contracts and pushes blood into a noncpmpliant ventricle - this creates vibrations that make the S4 sound **S4 occurs just before S1**