Week 4 - Chapter 14,15,16 Flashcards
(94 cards)
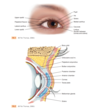
what is the skull ?
The skull is a rigid bony box that protects the brain and the special sense organs, it includes the bone of the cranium and the face
How many cranial bones do we have ? what are they named ?
there are 4 cranial bones: frontal, occipital, parietal, temporal
How do the cranial bones unite ?
They are meshed through immovable joints calleed sutures
How do the sutures develope ?
During birth, the cranial bones are not firmly jointed together to allow for the mobility and chnage in shape that is needed for the birth process
The sutures gradually ossify during early childhood
what are the different sutures present in the cranium ?
- Coronal Suture - crowns the head from ear to ear at the union of the frontal and parietal bones
- Saggittal suture - seperates the sides of the head lengthwise between the two parietal bones
- Lamboid Suture - seperates the parietal bones crosswise from the occipital bone
How many facial bones are there ? which one does not articulate at the sutures ?
there are 14 facial bones - the Mandible does not articulate with the sutures

what is the cranium supported by ? what is special about the C7 vertebrae ?
The cranium is supported by the cervical vertebrae (C1 atlas & c2 axis - all the way down to C7)
The C7 Vertebrae also has the name vertebrae prominens this is because it has an easily palpable long spinous process
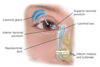
how many pairs of salivary glands are there ?
- Parotid Glands - found in the cheeks, mandible, anterior to and below the ear - they are the larges salivary glands
- Submandibular Glands - found beneath the manidble at the angle of the jaw
- Sublingual Glands - lie in the floor of glands
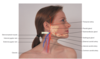
Where is the Temporal Artery located ?
Lies superior to the temporalis muscle and its pulsation is palpable anterior to the ear
what are the blood vessels located in the neck ?
- Internal Carotid Artery - which branches off the carotid artery ad run inward and upward to supply the brain
- External Carotid Artery - supplies the face, salivary glands, superficial temporal area
- Internal Jugular Vein - lies beneath the sternomstoid muscle along with the Carotid Artery
- External Jugular Vein - runs diagnolly across the sternomastoid muscle

What are the neck muscles ?
- Sternomastoid - divides each side of the neck into two triangles (anterior triagle - base is along the lower mandible and apex is at the suprasternal notch ) - (posterior triangle - behind the sternomastoid muscle - base is the clavicle ) - innervated by Cranial Nerve XI - accomplishes head rotation and head flexion
- Trapzeuis muscle - forms trapezoid shape on upper back - arises from occipital bone & vertebrae and extends fanning out onto scapula & Clavicle - move shoulders and extend and turn the nek
- Omohyiod Muscle
How many types of Trapezius muslces are there ? Where do they originate from? what is there function ?
There are two trapezius muscles - form trapezoid shape on the upper back - each of them arise from the occipital bone, the vertebrae
fans out from the scapula and clavicle
Trapzeius muscle moves the shoulders & extend & turn head
How is the sternomastoid muscle divided ?
The sternomastoid is divided into the anterior & posterior triangle
the anterior triangle lies in the front between the sternomastoid and the midline of the body
The posterior triangle is behind the sternomastoid muscle
What is the thyroid gland ?
The thyroid gland is an endocrie gland
straddles trachea in the middle of the neck
thyroid glad releases thyroxine (T4) Triiodothyronine(T3)
There are two thyroid lobes that are connected by the isthnus
What is thyroid Cartilage ?
The thyroid cartilage is the adams apple
The highest structure i the neck is the Hyoid Bone
how many lymph nodes are there ?
- Preauricular: in front of the ear
- Posterior Auricular (mastoid): superficial to mastoid process
- occipital: base of the skull
- submental: midline. behind the tip of the mandible
- submandibular: between the angle and the tip of mandible
- Tonsillar: under the angle of mandible
- Superficial Cervical: over;yin sternomastoid muscle
- Deep Cervical: deep uder sternomastoid muscle
- Posterior Cervical: in posterior triangle along the edge of the traps
- Supracavicular: just above and behind the clavicle

What is the importance of the lymphatic system ?
The lymphatic system is important for the bodies immune system - its job is to detect and eliminate the foreign substances from the body - the nodes filter the lymph
What are the four areas that are accessible for lymph examination?
- head & neck
- arms
- axillae
- ingiunal region
What are the developement changes for infants and children ?
Neonatal skull is seperated by stutures called Fontanelles (spaces where the suture intersects) - sutures ossify during the first year
during the fetal period had growth is rapid - the childs head grows reaching 90% of its final size when the child is 6 years old
facial bones grow at varying rates
lymphoid tissues grow to adult size at age 6
Lymphatic issues grows rapidly beyong adult size at ages 10 and 11 before puberty but then slowlies atrophies
What happens to women during pregnancy with regards to their thyroid gland ?
The thyroid gland enlarges slightly during pregnancy due to hyperplasia of the tissue and increased vascularity
What are some changes that occur in adults ?
facial bones and orbits appear more prominent
facial skin sags - decreases elasticity, subcutaneous fat, moisture
What are some questions that should be asked in regards to a headache ?
- any unsually frequent or severe headaches
- onset - when did the headache start
- gradual - over hours or a day or suddenly
- ever had this kind of headache before
- location of headache
- localized or on one side
- throbbing or aching pain
- mild, moderate, or severe
- course and duraion of headache
- how lond does it last
- what brings it on
- any other syptims associated with it
- any other illness
- medications
- what makes the pain worse
- pattern: any family history of headaches
- frequency of headaches
- what seems to help
What are some questions in regards to head injuries ?
- Onset: when
- Setting: any hazardous conditions ? were you wearig a helmet or hard hat?
- before injury - were you dizzy or lightheaded
- did you have a blackout or a seizure
- did you loss conciousness or fall
- knocked unconcious or did you fall and lose conciousness
- any history of illness
- where did you hit your head
- how long were you unconcious
- any symptoms after head injury (vomiting, headache)
- any change in the level of conciousness
- any associated synpotoms: discharge from ears or nose
- pattern: have the symptoms become worse
- effort to reat
15.
Questions to ask in regards to Dizziness ?
- describe the dizziness
- onset: abrupt or gradual ? after change in position
- associated factors