week 4 Flashcards
(24 cards)
Markowitz’s model suffers from several problems.
firstly
requires a huge number of estimates to fill the covariance matrix
applying it is computationally intensive, even if:
Only a relatively small numbers of assets are involved and / or;
The process is automated.
Markowitz Portfolio Selection Model.
method we use to identify the efficient set of portfolios
Markowitz’s model suffers from several problems.
secondly
does not provide any guideline to forecasting of the security risk premiums that are esesntial to construct the efficient frontier of risky assets
esp b/c past returns are unreliable guides to expected future returns
what does the single index model do?
simplifies way we describe sources of security risk allows us to use smaller, consistent sets of risk parameters and risk premiums
greatly enhance analysis of security risk premium
decompose risk into systematic and firm specific components –> helps simplify problem of estimating covariance and correlation
macroeconomic factor, m, and the result of firm-level surprises, ei, are
uncorrelated
beta, which is helpful in
estimating future systematic risk
alpha, however, we would not use it as a
alpha, however, we would not use it as a forecast for future alpha:
This is because evidence suggests that estimates from successive periods are essentially uncorrelated; and,
Instead, analysts must use security analysis to develop their expectation regarding future alpha
What does the CML graph?
CML graphs the risk premiums of efficient portfolios (i.e. portfolios composed of the market and the risk-free asset) as a function of portfolio standard deviation
What does SML graph?
SML graphs individual asset risk premiums as a function of asset risk.
expected return - beta relationship
SML valid for both efficient portfolios and individual assets
what does SML measure
SML provides benchmark for evaluation of investment performance
Provides required rate or return necessary to compensate investors for risk as well as the time value of money
Where do fairly priced assets lie?
Fairly priced assets will lie on the SML i.e. their expected returns are commensurate with their risk
When else do securities lie on the SML?
when market is in equilibrium all securities lie on the SML
SML
if stock is underpriced
it will provide an expected return in excess of the fair return stipulated on the SML
These stocks fall above the SML and have a positive alpha
SML
if stock is overpriced
Stocks providing an expected return less than the fair return are viewed as overpriced. These stocks fall below the SML and have a negative alpha.
The two key implications of the CAPM are:
The market portfolio is efficient; and,
The risk premium on a risky asset is proportional to its beta.
unlike the index model, the CAPM predicts
unlike the index model, the CAPM predicts that i will be zero for all assets.
How do we know if a stock has higher firm-specific risk?
Stock A has higher firm-specific risk because the deviations of the observations from the SCL are larger for Stock A than for Stock B. Deviations are measured by the vertical distance of each observation from the SCL
how do we know which stock has higher systematic risk?
Beta is the slope of the SCL, which is the measure of systematic risk. The SCL for Stock B is steeper; hence Stock B’s systematic risk is greater.
total variance is the sum of
the total variance is the sum of the explained variance plus the unexplained variance (the stock’s residual variance):
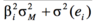
The R2(or squared correlation coefficient) of the SCL is
The R2 (or squared correlation coefficient) of the SCL is the ratio of the explained variance of the stock’s return to total variance, and the total variance is the sum of the explained variance plus the unexplained variance (the stock’s residual variance):

Alpha is
Alpha is the intercept of the SCL with the expected return axis. Stock A has a small positive alpha whereas Stock B has a negative alpha; hence, Stock A’s alpha is larger.
correlation coefficient is
simply the square root of R2, so Stock B’s correlation with the market is higher.
Firm-specific risk is measured by
Market risk is measured by
Firm-specific risk is measured by the residual standard deviation.
Market risk is measured by beta, the slope coefficient of the regression
R2 measures
R2 measures the fraction of total variance of return explained by the market return.


