7: Intestines Flashcards
(83 cards)
What is the difference in MOBILITY between the Small and Large intestines?
Small
- Duodenum NOT mobile
- Jejunum / Ileum mobile
Large
- Ascending & Descending colon NOT mobile
- Caecum NOT mobile
- Transverse colon mobile

What is the difference in Lumen Diameter between the Small and Large intestines?
Small: Smaller
Large: Larger

What is the difference in Logitudinal Muscle between the Small and Large intestines?
Small: Continuous layer
Large: 3 bands: teniae coli

What is the difference in FATTY TAGS between the Small and Large intestines?
Small: NONE
Large: Attached to wall

What is the difference in the WALLS between the Small and Large intestines?
Small: Smooth
Large: Sacculated (sac formation), forms Haustra (small pouches)

What is the difference in the Mucous Membrane between the Small and Large intestines?
Small: Permanent folds = plicae circularis
Large: Incomplete folds may be present

What is the difference in LYMPHATIC TISSUE between the Small and Large intestines?
Small: = lymphatic tissue
Large: NONE

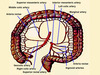
What is the blood supply of the DUODENUM? (2 things)
Duodenum derived from Foregut & Midgut
- Foregut supplied by Coeliac Trunk
Coeliac Trunk → Gastroduodenal Artery → Sup Pancreaticoduodenal Artery
- Midgut supplied by Sup Mesenteric Artery (SMA)
Abd. Aorta → SMA → Inf Pancreaticoduodenal Artery

What is the blood supply of the Jejunum and Ileum?
Jejunum & Ileum derived from Midgut
Midgut supplied by Sup Mesenteric Artery (SMA)
- Abd Aorta → SMA → Jejunal Arteries
- Abd Aorta → SMA → Ileal Arteries
Jejunal Arteries unite → form Arterial Arcades (loops)
Arterial Arcades give rise to Vasa Recta (straight arteries)
(Ileal arteries do same thing)

What is the venous drainage of the Duodenum? (2 points)
- Veins of duodenum follow arteries
- Drain → Hepatic Portal Vein:
- Directly
- Through Sup Mesenteric & Splenic Veins
What is the difference in COLOUR between the Jejunum and Ileum?
Jejunum: Deep red
Ileum: Paler pink

What is the difference in VASA RECTA between the Jejunum and Ileum?
Jejunum: Long
Ileum: Short

What is the difference in PLICAE CIRCULARIS FOLDS between the Jejunum and Ileum?
Jejunum: Large + Tall + Closely packed
Ileum: Low + Sparse + Absent in distal part

What is the difference in LYMPHOID NODULES (PEYERS PATCHES) between the Jejunum and Ileum?
Jejunum: Few
Ileum: Many
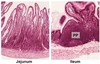
What is the difference in FAT IN MESENTRY between the Jejunum and Ileum?
Jejunum: Less
Ileum: More

What is the difference in LOOPS between the Jejunum and Ileum?
Jejunum: Few LARGE loops
Ileum: Many SHORT loops

What is the difference in VASCULARITY between the Jejunum and Ileum?
Jejunum: Greater
Ileum: Less

What is the difference in DIAMETER between the Jejunum and Ileum?
Jejunum: Thick and heavy
Ileum: Thin and light

What are the 8 parts of the large intestine?
- Caecum
- Appendix
- Ascending Colon
- Transverse Colon
- Descending Colon
- Sigmoid Colon
- Recum
- Anal Canal

What is the blood supply of the Caecum?
Caecum is Midgut derived
Midgut supplied by Sup Mesenteric Artery (SMA)
Abd Aorta → SMA → Ileocolic Artery

What is the blood supply of the Appendix?
Appendix is Midgut derived
Midgut supplied by Sup Mesenteric Artery (SMA)
Abd Aorta → SMA → Ileocolic Artery → Appendicular Artery

What is the venous drainage of the Caecum and Appendix?
Through Ileocolic Vein → Sup Mesenteric Vein (SMV) → Portal Vein
What is the blood supply of the Ascending Colon and Right Colic Flexture?
Ascending Colon and RCF derived from Midgut
Midgut supplied by Sup Mesenteric Artery (SMA)
- Abd Aorta → SMA → Ileocolic Artery (AC)
- Abd Aorta → SMA → Right Colic Artery (RCF)
How is the Marginal Artery of the large intestine formed?
3 arteries:
- Ileocolic Artery (supplies AC)
- Right Colic Artery (supplies RCF)
- Right branch of Middle Colic Artery (supplies TC)
Arteries anastamose with each other → Anastomotic Arcade
Asatomotic Arcade continues round large intestine to form a continuous arterial channel: Marginal Artery