Block 4 general Flashcards
(134 cards)
female genital ducts and glands derive from
UG sinus, paramesonephric ducts
what kind of process is sexual determination of female?
active
what supports persistence and devel of paramesonephric ducts?
estrogens
what does the unfused portion of the paramesonephric duct become?
uterine tubes
what does the fused portions of the paramesonephric duct become?
uterus and superior vagina
what develops from the UG sinus?
inferior vagina bladder, urethra, paraurethral glands, greater vestibular glands
bicornate uterus
incomplete fusion of the paramesonephric ducts
what happens to primitive sex cords in females?
primitive sex cords dissociate in females and second generation of cortical cords develop
where do the gonadal ridges appear?
gonadal (or “genital”) ridges appear on the medial surface of the urogenital ridges
what does the genital system consist of
gonads genital ducts and glands external genitalia
what are the three events initiating puberty
1) proper nutrition 2) gene activation 3) development of limbic system
A 15 year-old male does not demonstrate any signs of puberty. He is short for his age, his testicles show no evidence of enlargement, his testosterone levels are low, and he has a reduced ability to smell.
Kallmann syndrome
- KAL1 gene deficiency
- KAL1 induces migration of nerves from olfactory placode to olfactory bulb
- responsible for differentation and migration of GnRH secreting nerves
- Lack of GnRH results in ↓ LH, FSH, testosterone, sperm count
IGF-3
- allows descent of testes
- under influence of gene HOXA10
precocious puberty
premature development of genital organs and secondary sexual characteristics
- can be due to GnRH secreting tumor (optic glioma or hypothalmic astrocytoma)
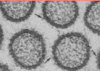
chromophils
- acidophils (40%)
- basophils (10%)
- part of pars distalis of the anterior pituitary
- ectoderm origin
- synthesize and secrete a variety of hormones
- each type generally secretes a single hormone
- arranged in cords; envolped by a delicate covering of connective tissue
- large cells, alot of RER, well developed Golgi complex, many secretion granules
- become chromophobes when they dump their hormones
chromophobe
chlorophils that have released their specific hormones and are “degranulated” and thus stain poorly
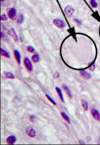
Identify

Chromophils
- large cells, much RER,well developed Golgi complex, many secretion granules (contain hormone)
Idenitfy circled structure

Chromophobe
- chromophils that have released their specific hormones and are “degranulated”
- therefore, stain poorly
Steroidogenic TF
promotes gonadotroph lineage
T-box TF (“Tpit”)
promotes the corticotroph lineage
POU1F1
- encodes a POU domain
- this domain is essential for differentiation and expansion of somatotrophs, lactotrophs and thyrotrophs
- transcription factor
- mutations - responsbile for GH, PRL and TSH deficiencies
supraoptic nuclei
ADH
Paraventricular nuclei
oxytocin
hypothalamic nuclei
cell bodies of neurosecretory neurons that releasing or release-inhibiting hormones are synthesized